GPU 视频解码器/编码器¶
作者: Moto Hira
本教程介绍如何将 NVIDIA 的硬件视频解码器 (NVDEC) 和编码器 (NVENC) 与 TorchAudio 结合使用。
使用硬件编码器/解码器可以提高加载和保存某些类型视频的速度。
在 TorchAduio 中使用它们需要使用 NVENC/NVDEC 支持构建的 FFmpeg。Google Colab 预装了这样的 FFmpeg,所以你可以在 Google Colab 上运行本教程。
如果要启用 GPU 解码/编码,请参考 启用 GPU 视频解码器/编码器。
使用 nightly 版本更新 PyTorch 和 TorchAudio¶
在 PyTorch 2.0 发布之前,我们需要使用 PyTorch 和 TorchAudio 的夜间版本。
[2]:
%%bash
pip uninstall -y -q torch torchaudio torchvision torchtext
pip install --progress-bar off --pre torch torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu117 2> /dev/null
Looking in indexes: https://pypi.org/simple, https://us-python.pkg.dev/colab-wheels/public/simple/, https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu117
Collecting torch
Downloading https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu117/torch-2.0.0.dev20230209%2Bcu117-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl (1837.7 MB)
Collecting torchaudio
Downloading https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu117/torchaudio-2.0.0.dev20230208%2Bcu117-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl (4.4 MB)
Requirement already satisfied: filelock in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (from torch) (3.9.0)
Collecting pytorch-triton==2.0.0+0d7e753227
Downloading https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/pytorch_triton-2.0.0%2B0d7e753227-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl (18.7 MB)
Requirement already satisfied: typing-extensions in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (from torch) (4.4.0)
Requirement already satisfied: networkx in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (from torch) (3.0)
Requirement already satisfied: sympy in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (from torch) (1.7.1)
Requirement already satisfied: cmake in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (from pytorch-triton==2.0.0+0d7e753227->torch) (3.22.6)
Requirement already satisfied: mpmath>=0.19 in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (from sympy->torch) (1.2.1)
Installing collected packages: pytorch-triton, torch, torchaudio
Successfully installed pytorch-triton-2.0.0+0d7e753227 torch-2.0.0.dev20230209+cu117 torchaudio-2.0.0.dev20230208+cu117
安装第三方库并下载资源¶
[8]:
%%bash
pip3 install --progress-bar off boto3 2> /dev/null
Looking in indexes: https://pypi.org/simple, https://us-python.pkg.dev/colab-wheels/public/simple/
Collecting boto3
Downloading boto3-1.26.67-py3-none-any.whl (132 kB)
Collecting botocore<1.30.0,>=1.29.67
Downloading botocore-1.29.67-py3-none-any.whl (10.4 MB)
Collecting jmespath<2.0.0,>=0.7.1
Downloading jmespath-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (20 kB)
Collecting s3transfer<0.7.0,>=0.6.0
Downloading s3transfer-0.6.0-py3-none-any.whl (79 kB)
Requirement already satisfied: python-dateutil<3.0.0,>=2.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (from botocore<1.30.0,>=1.29.67->boto3) (2.8.2)
Collecting urllib3<1.27,>=1.25.4
Downloading urllib3-1.26.14-py2.py3-none-any.whl (140 kB)
Requirement already satisfied: six>=1.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (from python-dateutil<3.0.0,>=2.1->botocore<1.30.0,>=1.29.67->boto3) (1.15.0)
Installing collected packages: urllib3, jmespath, botocore, s3transfer, boto3
Attempting uninstall: urllib3
Found existing installation: urllib3 1.24.3
Uninstalling urllib3-1.24.3:
Successfully uninstalled urllib3-1.24.3
Successfully installed boto3-1.26.67 botocore-1.29.67 jmespath-1.0.1 s3transfer-0.6.0 urllib3-1.26.14
[10]:
%%bash
wget -q -O input.mp4 "https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/tutorial-assets/stream-api/NASAs_Most_Scientifically_Complex_Space_Observatory_Requires_Precision-MP4_small.mp4"
检查可用的 GPU¶
[1]:
%%bash
nvidia-smi
Thu Feb 9 15:54:05 2023
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 510.47.03 Driver Version: 510.47.03 CUDA Version: 11.6 |
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|===============================+======================+======================|
| 0 Tesla T4 Off | 00000000:00:04.0 Off | 0 |
| N/A 58C P0 28W / 70W | 0MiB / 15360MiB | 0% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=============================================================================|
| No running processes found |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
检查 FFmpeg 安装¶
让我们进行快速的健全性检查,以确认我们构建的 FFmpeg 可以正常工作。
[55]:
%%bash
ffmpeg -hide_banner -decoders | grep -i cuvid
V..... h264_cuvid Nvidia CUVID H264 decoder (codec h264)
V..... hevc_cuvid Nvidia CUVID HEVC decoder (codec hevc)
V..... mjpeg_cuvid Nvidia CUVID MJPEG decoder (codec mjpeg)
V..... mpeg1_cuvid Nvidia CUVID MPEG1VIDEO decoder (codec mpeg1video)
V..... mpeg2_cuvid Nvidia CUVID MPEG2VIDEO decoder (codec mpeg2video)
V..... mpeg4_cuvid Nvidia CUVID MPEG4 decoder (codec mpeg4)
V..... vc1_cuvid Nvidia CUVID VC1 decoder (codec vc1)
V..... vp8_cuvid Nvidia CUVID VP8 decoder (codec vp8)
V..... vp9_cuvid Nvidia CUVID VP9 decoder (codec vp9)
[56]:
%%bash
ffmpeg -hide_banner -encoders | grep -i nvenc
V..... h264_nvenc NVIDIA NVENC H.264 encoder (codec h264)
V..... nvenc NVIDIA NVENC H.264 encoder (codec h264)
V..... nvenc_h264 NVIDIA NVENC H.264 encoder (codec h264)
V..... nvenc_hevc NVIDIA NVENC hevc encoder (codec hevc)
V..... hevc_nvenc NVIDIA NVENC hevc encoder (codec hevc)
以下命令从远程服务器获取视频,使用 NVDEC (cuvid) 解码并使用 NVENC 重新编码。如果此命令不起作用,则 FFmpeg 安装存在问题,TorchAudio 也无法使用它们。
[5]:
%%bash
ffmpeg -hide_banner -y -vsync 0 -hwaccel cuvid -hwaccel_output_format cuda -c:v h264_cuvid -resize 360x240 -i "https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/tutorial-assets/stream-api/NASAs_Most_Scientifically_Complex_Space_Observatory_Requires_Precision-MP4_small.mp4" -c:a copy -c:v h264_nvenc -b:v 5M test.mp4
Input #0, mov,mp4,m4a,3gp,3g2,mj2, from 'https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/tutorial-assets/stream-api/NASAs_Most_Scientifically_Complex_Space_Observatory_Requires_Precision-MP4_small.mp4':
Metadata:
major_brand : mp42
minor_version : 512
compatible_brands: mp42iso2avc1mp41
encoder : Lavf58.76.100
Duration: 00:03:26.04, start: 0.000000, bitrate: 1294 kb/s
Stream #0:0(eng): Video: h264 (High) (avc1 / 0x31637661), yuv420p(tv, bt709), 960x540 [SAR 1:1 DAR 16:9], 1156 kb/s, 29.97 fps, 29.97 tbr, 30k tbn, 59.94 tbc (default)
Metadata:
handler_name : ?Mainconcept Video Media Handler
Stream #0:1(eng): Audio: aac (LC) (mp4a / 0x6134706D), 48000 Hz, stereo, fltp, 128 kb/s (default)
Metadata:
handler_name : #Mainconcept MP4 Sound Media Handler
Stream mapping:
Stream #0:0 -> #0:0 (h264 (h264_cuvid) -> h264 (h264_nvenc))
Stream #0:1 -> #0:1 (copy)
Press [q] to stop, [?] for help
Output #0, mp4, to 'test.mp4':
Metadata:
major_brand : mp42
minor_version : 512
compatible_brands: mp42iso2avc1mp41
encoder : Lavf58.29.100
Stream #0:0(eng): Video: h264 (h264_nvenc) (Main) (avc1 / 0x31637661), cuda, 360x240 [SAR 1:1 DAR 3:2], q=-1--1, 5000 kb/s, 29.97 fps, 30k tbn, 29.97 tbc (default)
Metadata:
handler_name : ?Mainconcept Video Media Handler
encoder : Lavc58.54.100 h264_nvenc
Side data:
cpb: bitrate max/min/avg: 0/0/5000000 buffer size: 10000000 vbv_delay: -1
Stream #0:1(eng): Audio: aac (LC) (mp4a / 0x6134706D), 48000 Hz, stereo, fltp, 128 kb/s (default)
Metadata:
handler_name : #Mainconcept MP4 Sound Media Handler
frame= 6175 fps=1673 q=8.0 Lsize= 41278kB time=00:03:26.17 bitrate=1640.1kbits/s speed=55.9x
video:37869kB audio:3234kB subtitle:0kB other streams:0kB global headers:0kB muxing overhead: 0.424815%
检查 TorchAudio / FFmpeg 集成¶
[6]:
import torch
import torchaudio
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
from torchaudio.io import StreamReader, StreamWriter
2.0.0.dev20230209+cu117
2.0.0.dev20230208+cu117
[61]:
from torchaudio.utils import ffmpeg_utils
print("Library versions:")
print(ffmpeg_utils.get_versions())
print("\nBuild config:")
print(ffmpeg_utils.get_build_config())
print("\nDecoders:")
print([k for k in ffmpeg_utils.get_video_decoders().keys() if "cuvid" in k])
print("\nEncoders:")
print([k for k in ffmpeg_utils.get_video_encoders().keys() if "nvenc" in k])
Library versions:
{'libavutil': (56, 31, 100), 'libavcodec': (58, 54, 100), 'libavformat': (58, 29, 100), 'libavfilter': (7, 57, 100), 'libavdevice': (58, 8, 100)}
Build config:
--prefix=/usr --extra-version=0ubuntu0.1 --toolchain=hardened --libdir=/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu --incdir=/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu --arch=amd64 --enable-gpl --disable-stripping --enable-avresample --disable-filter=resample --enable-avisynth --enable-gnutls --enable-ladspa --enable-libaom --enable-libass --enable-libbluray --enable-libbs2b --enable-libcaca --enable-libcdio --enable-libcodec2 --enable-libflite --enable-libfontconfig --enable-libfreetype --enable-libfribidi --enable-libgme --enable-libgsm --enable-libjack --enable-libmp3lame --enable-libmysofa --enable-libopenjpeg --enable-libopenmpt --enable-libopus --enable-libpulse --enable-librsvg --enable-librubberband --enable-libshine --enable-libsnappy --enable-libsoxr --enable-libspeex --enable-libssh --enable-libtheora --enable-libtwolame --enable-libvidstab --enable-libvorbis --enable-libvpx --enable-libwavpack --enable-libwebp --enable-libx265 --enable-libxml2 --enable-libxvid --enable-libzmq --enable-libzvbi --enable-lv2 --enable-omx --enable-openal --enable-opencl --enable-opengl --enable-sdl2 --enable-libdc1394 --enable-libdrm --enable-libiec61883 --enable-nvenc --enable-chromaprint --enable-frei0r --enable-libx264 --enable-shared
Decoders:
['h264_cuvid', 'hevc_cuvid', 'mjpeg_cuvid', 'mpeg1_cuvid', 'mpeg2_cuvid', 'mpeg4_cuvid', 'vc1_cuvid', 'vp8_cuvid', 'vp9_cuvid']
Encoders:
['h264_nvenc', 'nvenc', 'nvenc_h264', 'nvenc_hevc', 'hevc_nvenc']
GPU 编码和解码基准测试¶
现在 FFmpeg 和生成的库已准备就绪,我们使用 TorchAudio 测试 NVDEC/NVENC。有关 TorchAudio 的流式处理 API 的基础知识,请参阅 Media I/O 教程。
[7]:
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
对 NVDEC 进行基准测试StreamReader¶
首先,我们测试硬件解码,然后从多个位置(本地文件、网络文件、AWS S3)获取视频,并使用 NVDEC 对它们进行解码。
[9]:
import boto3
from botocore import UNSIGNED
from botocore.config import Config
print(boto3.__version__)
1.26.67
首先,我们定义将用于测试的函数。
Funcion 从头到尾对给定的源进行解码,并报告经过的时间,并返回一个图像 frmae 作为样本。test_decode
[11]:
result = torch.zeros((4, 2))
samples = [[None, None] for _ in range(4)]
def test_decode(src, config, i_sample):
print("=" * 40)
print("* Configuration:", config)
print("* Source:", src)
print("=" * 40)
t0 = time.monotonic()
s = StreamReader(src)
s.add_video_stream(5, **config)
num_frames = 0
for i, (chunk, ) in enumerate(s.stream()):
if i == 0:
print(' - Chunk:', chunk.shape, chunk.device, chunk.dtype)
if i == i_sample:
sample = chunk[0]
num_frames += chunk.shape[0]
elapsed = time.monotonic() - t0
print()
print(f" - Processed {num_frames} frames.")
print(f" - Elapsed: {elapsed} seconds.")
print()
return elapsed, sample
从本地文件解码 MP4¶
对于第一个测试,我们比较了 CPU 和 NVDEC 解码 250MB MP4 视频所需的时间。
[12]:
local_src = "input.mp4"
i_sample = 520
中央处理器¶
[13]:
cpu_conf = {
"decoder": "h264", # CPU decoding
}
elapsed, sample = test_decode(local_src, cpu_conf, i_sample)
========================================
* Configuration: {'decoder': 'h264'}
* Source: input.mp4
========================================
- Chunk: torch.Size([5, 3, 540, 960]) cpu torch.uint8
- Processed 6175 frames.
- Elapsed: 43.65067997 seconds.
[14]:
result[0, 0] = elapsed
samples[0][0] = sample
CUDA 的¶
[15]:
cuda_conf = {
"decoder": "h264_cuvid", # Use CUDA HW decoder
"hw_accel": "cuda:0", # Then keep the memory on CUDA:0
}
elapsed, sample = test_decode(local_src, cuda_conf, i_sample)
========================================
* Configuration: {'decoder': 'h264_cuvid', 'hw_accel': 'cuda:0'}
* Source: input.mp4
========================================
- Chunk: torch.Size([5, 3, 540, 960]) cuda:0 torch.uint8
- Processed 6175 frames.
- Elapsed: 5.754925530000008 seconds.
[16]:
result[0, 1] = elapsed
samples[0][1] = sample
从网络解码 MP4¶
让我们对通过网络动态检索的源运行相同的测试。
[17]:
network_src = "https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/tutorial-assets/stream-api/NASAs_Most_Scientifically_Complex_Space_Observatory_Requires_Precision-MP4_small.mp4"
i_sample = 750
中央处理器¶
[18]:
elapsed, sample = test_decode(network_src, cpu_conf, i_sample)
========================================
* Configuration: {'decoder': 'h264'}
* Source: https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/tutorial-assets/stream-api/NASAs_Most_Scientifically_Complex_Space_Observatory_Requires_Precision-MP4_small.mp4
========================================
- Chunk: torch.Size([5, 3, 540, 960]) cpu torch.uint8
- Processed 6175 frames.
- Elapsed: 33.74701378400002 seconds.
[19]:
result[1, 0] = elapsed
samples[1][0] = sample
CUDA 的¶
[20]:
elapsed, sample = test_decode(network_src, cuda_conf, i_sample)
========================================
* Configuration: {'decoder': 'h264_cuvid', 'hw_accel': 'cuda:0'}
* Source: https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/tutorial-assets/stream-api/NASAs_Most_Scientifically_Complex_Space_Observatory_Requires_Precision-MP4_small.mp4
========================================
- Chunk: torch.Size([5, 3, 540, 960]) cuda:0 torch.uint8
- Processed 6175 frames.
- Elapsed: 15.769149663000007 seconds.
[21]:
result[1, 1] = elapsed
samples[1][1] = sample
直接从 S4 解码 MP3¶
使用类似文件的对象输入,我们可以获取存储在 AWS S3 上的视频并对其进行解码,而无需将其保存在本地文件系统上。
[22]:
bucket = "pytorch"
key = "torchaudio/tutorial-assets/stream-api/NASAs_Most_Scientifically_Complex_Space_Observatory_Requires_Precision-MP4_small.mp4"
s3_client = boto3.client("s3", config=Config(signature_version=UNSIGNED))
i_sample = 115
定义 Helper 类¶
StreamReader 支持具有 method 的类文件对象。除此之外,如果类文件对象具有 method,则 StreamReader 会尝试使用它来更可靠地检测媒体格式。readseek
但是,的 S3 客户端响应对象的 seek 方法仅引发错误,以告知用户不支持 seek作。因此,我们用一个没有 method 的类来包装它。这样,StreamReader 就不会尝试使用该方法。boto3seekseek
注意
由于流式处理的性质,当使用没有 seek 方法的类文件对象时,不支持某些格式。例如,MP4 格式在文件的开头或结尾包含元数据。如果元数据位于末尾,则 StreamReader 无法解码流。seek
[23]:
# Wrapper to hide the native `seek` method of boto3, which
# only raises an error.
class UnseekableWrapper:
def __init__(self, obj):
self.obj = obj
def read(self, n):
return self.obj.read(n)
def __str__(self):
return str(self.obj)
中央处理器¶
[24]:
response = s3_client.get_object(Bucket=bucket, Key=key)
src = UnseekableWrapper(response["Body"])
elapsed, sample = test_decode(src, cpu_conf, i_sample)
========================================
* Configuration: {'decoder': 'h264'}
* Source: <botocore.response.StreamingBody object at 0x7fcc9b0b83a0>
========================================
- Chunk: torch.Size([5, 3, 540, 960]) cpu torch.uint8
- Processed 6175 frames.
- Elapsed: 29.465254898000012 seconds.
[25]:
result[2, 0] = elapsed
samples[2][0] = sample
CUDA 的¶
[26]:
response = s3_client.get_object(Bucket=bucket, Key=key)
src = UnseekableWrapper(response["Body"])
elapsed, sample = test_decode(src, cuda_conf, i_sample)
========================================
* Configuration: {'decoder': 'h264_cuvid', 'hw_accel': 'cuda:0'}
* Source: <botocore.response.StreamingBody object at 0x7fcc9b0b8730>
========================================
- Chunk: torch.Size([5, 3, 540, 960]) cuda:0 torch.uint8
- Processed 6175 frames.
- Elapsed: 3.475249672000018 seconds.
[27]:
result[2, 1] = elapsed
samples[2][1] = sample
解码和调整大小¶
在下一个测试中,我们添加预处理。NVDEC 支持多种预处理方案,这些方案也在所选硬件上执行。对于 CPU,我们通过 FFmpeg 的 filter graph 应用相同类型的软件预处理。
[28]:
i_sample = 1085
中央处理器¶
[29]:
cpu_conf = {
"decoder": "h264", # CPU decoding
"filter_desc": "scale=360:240", # Software filter
}
elapsed, sample = test_decode(local_src, cpu_conf, i_sample)
========================================
* Configuration: {'decoder': 'h264', 'filter_desc': 'scale=360:240'}
* Source: input.mp4
========================================
- Chunk: torch.Size([5, 3, 240, 360]) cpu torch.uint8
- Processed 6175 frames.
- Elapsed: 17.26762169899996 seconds.
[30]:
result[3, 0] = elapsed
samples[3][0] = sample
CUDA 的¶
[31]:
cuda_conf = {
"decoder": "h264_cuvid", # Use CUDA HW decoder
"decoder_option": {
"resize": "360x240", # Then apply HW preprocessing (resize)
},
"hw_accel": "cuda:0", # Then keep the memory on CUDA:0
}
elapsed, sample = test_decode(local_src, cuda_conf, i_sample)
========================================
* Configuration: {'decoder': 'h264_cuvid', 'decoder_option': {'resize': '360x240'}, 'hw_accel': 'cuda:0'}
* Source: input.mp4
========================================
- Chunk: torch.Size([5, 3, 240, 360]) cuda:0 torch.uint8
- Processed 6175 frames.
- Elapsed: 15.233130482000035 seconds.
[32]:
result[3, 1] = elapsed
samples[3][1] = sample
结果¶
下表总结了使用 CPU 和 NVDEC 解码同一介质所花费的时间。我们看到 NVDEC 的加速速度显著加快。
[33]:
res = pd.DataFrame(
result.numpy(),
index=["Decoding (local file)", "Decoding (network file)", "Decoding (file-like object, S3)", "Decoding + Resize"],
columns=["CPU", "NVDEC"],
)
print(res)
CPU NVDEC
Decoding (local file) 43.650681 5.754926
Decoding (network file) 33.747013 15.769150
Decoding (file-like object, S3) 29.465256 3.475250
Decoding + Resize 17.267622 15.233130
以下代码显示了 CPU 解码和 NVDEC 生成的一些帧。它们产生的结果看似相同。
[34]:
def yuv_to_rgb(img):
img = img.cpu().to(torch.float)
y = img[..., 0, :, :]
u = img[..., 1, :, :]
v = img[..., 2, :, :]
y /= 255
u = u / 255 - 0.5
v = v / 255 - 0.5
r = y + 1.14 * v
g = y + -0.396 * u - 0.581 * v
b = y + 2.029 * u
rgb = torch.stack([r, g, b], -1)
rgb = (rgb * 255).clamp(0, 255).to(torch.uint8)
return rgb.numpy()
[35]:
f, axs = plt.subplots(4, 2, figsize=[12.8, 19.2])
for i in range(4):
for j in range(2):
axs[i][j].imshow(yuv_to_rgb(samples[i][j]))
axs[i][j].set_title(
f"{'CPU' if j == 0 else 'NVDEC'}{' with resize' if i == 3 else ''}")
plt.plot(block=False)
[35]:
[]

对 NVENC 进行基准测试StreamWriter¶
接下来,我们使用 StreamWriter 和 NVENC 对编码速度进行基准测试。
[36]:
def test_encode(data, dst, **config):
print("=" * 40)
print("* Configuration:", config)
print("* Destination:", dst)
print("=" * 40)
t0 = time.monotonic()
s = StreamWriter(dst)
s.add_video_stream(**config)
with s.open():
s.write_video_chunk(0, data)
elapsed = time.monotonic() - t0
print()
print(f" - Processed {len(data)} frames.")
print(f" - Elapsed: {elapsed} seconds.")
print()
return elapsed
result = torch.zeros((3, 3))
我们用于生成测试数据。StreamReader
[37]:
def get_data(frame_rate, height, width, format, duration=15):
src = f"testsrc2=rate={frame_rate}:size={width}x{height}:duration={duration}"
s = StreamReader(src=src, format="lavfi")
s.add_basic_video_stream(-1, format=format)
s.process_all_packets()
video, = s.pop_chunks()
return video
对 MP4 - 360P 进行编码¶
对于第一个测试,我们比较了 CPU 和 NVENC 编码 15 秒的小分辨率视频所需的时间。
[38]:
pict_config = {
"height": 360,
"width": 640,
"frame_rate": 30000/1001,
"format": "yuv444p",
}
video = get_data(**pict_config)
中央处理器¶
[39]:
encode_config = {
"encoder": "libx264",
"encoder_format": "yuv444p",
}
result[0, 0] = test_encode(video, "360p_cpu.mp4", **pict_config, **encode_config)
========================================
* Configuration: {'height': 360, 'width': 640, 'frame_rate': 29.97002997002997, 'format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder': 'libx264', 'encoder_format': 'yuv444p'}
* Destination: 360p_cpu.mp4
========================================
- Processed 450 frames.
- Elapsed: 6.311792093000008 seconds.
CUDA(来自 CPU Tensor)¶
现在我们测试 NVENC。这一次,数据作为编码的一部分从 CPU 内存发送到 GPU 内存。
[40]:
encode_config = {
"encoder": "h264_nvenc", # Use NVENC
"encoder_format": "yuv444p",
"encoder_option": {"gpu": "0"}, # Run encoding on the cuda:0 device
}
result[1, 0] = test_encode(video, "360p_cuda.mp4", **pict_config, **encode_config)
========================================
* Configuration: {'height': 360, 'width': 640, 'frame_rate': 29.97002997002997, 'format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder': 'h264_nvenc', 'encoder_format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder_option': {'gpu': '0'}}
* Destination: 360p_cuda.mp4
========================================
- Processed 450 frames.
- Elapsed: 0.5352325430000064 seconds.
CUDA (来自 CUDA Tensor)¶
如果数据已经存在于 CUDA 上,那么我们可以直接将其传递给 GPU 编码器。
[41]:
device = "cuda:0"
encode_config = {
"encoder": "h264_nvenc", # GPU Encoder
"encoder_format": "yuv444p",
"encoder_option": {"gpu": "0"}, # Run encoding on the cuda:0 device
"hw_accel": device, # Data comes from cuda:0 device
}
result[2, 0] = test_encode(video.to(torch.device(device)), "360p_cuda_hw.mp4", **pict_config, **encode_config)
========================================
* Configuration: {'height': 360, 'width': 640, 'frame_rate': 29.97002997002997, 'format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder': 'h264_nvenc', 'encoder_format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder_option': {'gpu': '0'}, 'hw_accel': 'cuda:0'}
* Destination: 360p_cuda_hw.mp4
========================================
- Processed 450 frames.
- Elapsed: 0.7045466739999711 seconds.
编码 MP4 - 720P¶
让我们对具有更高分辨率的视频运行相同的测试。
[42]:
pict_config = {
"height": 720,
"width": 1280,
"frame_rate": 30000/1001,
"format": "yuv444p",
}
video = get_data(**pict_config)
中央处理器¶
[43]:
encode_config = {
"encoder": "libx264",
"encoder_format": "yuv444p",
}
result[0, 1] = test_encode(video, "720p_cpu.mp4", **pict_config, **encode_config)
========================================
* Configuration: {'height': 720, 'width': 1280, 'frame_rate': 29.97002997002997, 'format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder': 'libx264', 'encoder_format': 'yuv444p'}
* Destination: 720p_cpu.mp4
========================================
- Processed 450 frames.
- Elapsed: 14.017578084000036 seconds.
CUDA(来自 CPU Tensor)¶
[44]:
encode_config = {
"encoder": "h264_nvenc",
"encoder_format": "yuv444p",
}
result[1, 1] = test_encode(video, "720p_cuda.mp4", **pict_config, **encode_config)
========================================
* Configuration: {'height': 720, 'width': 1280, 'frame_rate': 29.97002997002997, 'format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder': 'h264_nvenc', 'encoder_format': 'yuv444p'}
* Destination: 720p_cuda.mp4
========================================
- Processed 450 frames.
- Elapsed: 0.9797491379999883 seconds.
CUDA (来自 CUDA Tensor)¶
[45]:
device = "cuda:0"
encode_config = {
"encoder": "h264_nvenc",
"encoder_format": "yuv444p",
"encoder_option": {"gpu": "0"},
"hw_accel": device,
}
result[2, 1] = test_encode(video.to(torch.device(device)), "720p_cuda_hw.mp4", **pict_config, **encode_config)
========================================
* Configuration: {'height': 720, 'width': 1280, 'frame_rate': 29.97002997002997, 'format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder': 'h264_nvenc', 'encoder_format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder_option': {'gpu': '0'}, 'hw_accel': 'cuda:0'}
* Destination: 720p_cuda_hw.mp4
========================================
- Processed 450 frames.
- Elapsed: 0.7259890020000057 seconds.
编码 MP4 - 1080P¶
我们制作了更大的视频。
[46]:
pict_config = {
"height": 1080,
"width": 1920,
"frame_rate": 30000/1001,
"format": "yuv444p",
}
video = get_data(**pict_config)
中央处理器¶
[47]:
encode_config = {
"encoder": "libx264",
"encoder_format": "yuv444p",
}
result[0, 2] = test_encode(video, "1080p_cpu.mp4", **pict_config, **encode_config)
========================================
* Configuration: {'height': 1080, 'width': 1920, 'frame_rate': 29.97002997002997, 'format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder': 'libx264', 'encoder_format': 'yuv444p'}
* Destination: 1080p_cpu.mp4
========================================
- Processed 450 frames.
- Elapsed: 29.441768007999997 seconds.
CUDA(来自 CPU Tensor)¶
[48]:
encode_config = {
"encoder": "h264_nvenc",
"encoder_format": "yuv444p",
}
result[1, 2] = test_encode(video, "1080p_cuda.mp4", **pict_config, **encode_config)
========================================
* Configuration: {'height': 1080, 'width': 1920, 'frame_rate': 29.97002997002997, 'format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder': 'h264_nvenc', 'encoder_format': 'yuv444p'}
* Destination: 1080p_cuda.mp4
========================================
- Processed 450 frames.
- Elapsed: 1.5768605540000067 seconds.
CUDA (来自 CUDA Tensor)¶
[49]:
device = "cuda:0"
encode_config = {
"encoder": "h264_nvenc",
"encoder_format": "yuv444p",
"encoder_option": {"gpu": "0"},
"hw_accel": device,
}
result[2, 2] = test_encode(video.to(torch.device(device)), "1080p_cuda_hw.mp4", **pict_config, **encode_config)
========================================
* Configuration: {'height': 1080, 'width': 1920, 'frame_rate': 29.97002997002997, 'format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder': 'h264_nvenc', 'encoder_format': 'yuv444p', 'encoder_option': {'gpu': '0'}, 'hw_accel': 'cuda:0'}
* Destination: 1080p_cuda_hw.mp4
========================================
- Processed 450 frames.
- Elapsed: 1.4002963130000126 seconds.
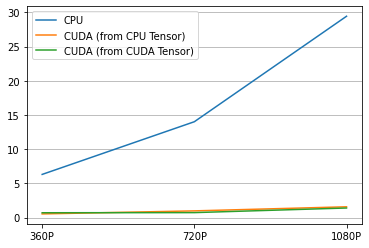
结果¶
这是结果。
[50]:
labels = ["CPU", "CUDA (from CPU Tensor)", "CUDA (from CUDA Tensor)"]
columns = ["360P", "720P", "1080P"]
res = pd.DataFrame(
result.numpy(),
index=labels,
columns=columns,
)
print(res)
360P 720P 1080P
CPU 6.311792 14.017578 29.441769
CUDA (from CPU Tensor) 0.535233 0.979749 1.576861
CUDA (from CUDA Tensor) 0.704547 0.725989 1.400296
[51]:
plt.plot(result.T)
plt.legend(labels)
plt.xticks([i for i in range(3)], columns)
plt.grid(visible=True, axis='y')
生成的视频如下所示。
[52]:
from IPython.display import HTML
HTML('''
<div>
<video width=360 controls autoplay>
<source src="https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/tutorial-assets/streamwriter_360p_cpu.mp4" type="video/mp4">
</video>
<video width=360 controls autoplay>
<source src="https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/tutorial-assets/streamwriter_360p_cuda.mp4" type="video/mp4">
</video>
<video width=360 controls autoplay>
<source src="https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/tutorial-assets/streamwriter_360p_cuda_hw.mp4" type="video/mp4">
</video>
</div>
''')
[52]:
结论¶
我们研究了如何构建支持 NVDEC/NVENC 的 FFmpeg 库,并从 TorchAudio 使用它们。NVDEC/NVENC 在保存/加载视频时提供了显着的速度。