注意
单击此处下载完整的示例代码
StreamReader 高级用法¶
作者: Moto Hira
本教程是 StreamReader 基本用法的延续。
这演示如何使用StreamReader为
设备输入,例如麦克风、网络摄像头和屏幕录制
生成合成音频/视频
使用自定义筛选条件表达式应用预处理
import torch
import torchaudio
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
import IPython
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torchaudio.io import StreamReader
base_url = "https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/tutorial-assets"
AUDIO_URL = f"{base_url}/Lab41-SRI-VOiCES-src-sp0307-ch127535-sg0042.wav"
VIDEO_URL = f"{base_url}/stream-api/NASAs_Most_Scientifically_Complex_Space_Observatory_Requires_Precision-MP4.mp4"
2.5.0
2.5.0
音频/视频设备输入¶
鉴于系统具有适当的媒体设备,并且 libavdevice 是 配置为使用设备,流式处理 API 可以 从这些设备中提取媒体流。
为此,我们将额外的参数传递给构造函数。 指定 Device 组件,而 Dictionary 特定于指定的组件。formatoptionformatoption
要传递的确切参数取决于系统配置。 有关详细信息,请参阅 https://ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg-devices.html。
以下示例说明了如何在 MacBook Pro 上执行此作。
首先,我们需要检查可用的设备。
$ ffmpeg -f avfoundation -list_devices true -i ""
[AVFoundation indev @ 0x143f04e50] AVFoundation video devices:
[AVFoundation indev @ 0x143f04e50] [0] FaceTime HD Camera
[AVFoundation indev @ 0x143f04e50] [1] Capture screen 0
[AVFoundation indev @ 0x143f04e50] AVFoundation audio devices:
[AVFoundation indev @ 0x143f04e50] [0] MacBook Pro Microphone
我们使用 FaceTime 高清摄像头作为视频设备(索引 0),使用 MacBook Pro 麦克风作为音频设备(索引 0)。
如果我们不传递 any ,则设备使用其默认的
配置。解码器可能不支持该配置。option
>>> StreamReader(
... src="0:0", # The first 0 means `FaceTime HD Camera`, and
... # the second 0 indicates `MacBook Pro Microphone`.
... format="avfoundation",
... )
[avfoundation @ 0x125d4fe00] Selected framerate (29.970030) is not supported by the device.
[avfoundation @ 0x125d4fe00] Supported modes:
[avfoundation @ 0x125d4fe00] 1280x720@[1.000000 30.000000]fps
[avfoundation @ 0x125d4fe00] 640x480@[1.000000 30.000000]fps
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
...
RuntimeError: Failed to open the input: 0:0
通过提供 ,我们可以更改设备的格式
流转换为 Decoder 支持的格式。option
>>> streamer = StreamReader(
... src="0:0",
... format="avfoundation",
... option={"framerate": "30", "pixel_format": "bgr0"},
... )
>>> for i in range(streamer.num_src_streams):
... print(streamer.get_src_stream_info(i))
SourceVideoStream(media_type='video', codec='rawvideo', codec_long_name='raw video', format='bgr0', bit_rate=0, width=640, height=480, frame_rate=30.0)
SourceAudioStream(media_type='audio', codec='pcm_f32le', codec_long_name='PCM 32-bit floating point little-endian', format='flt', bit_rate=3072000, sample_rate=48000.0, num_channels=2)
合成源流¶
作为设备集成的一部分,ffmpeg 提供了一个 “虚拟设备” 接口。此接口提供合成音频/视频数据 生成。
为此,我们设置并提供过滤器描述
自。format=lavfisrc
过滤器描述的详细信息可以在 https://ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg-filters.html 中找到
音频示例¶
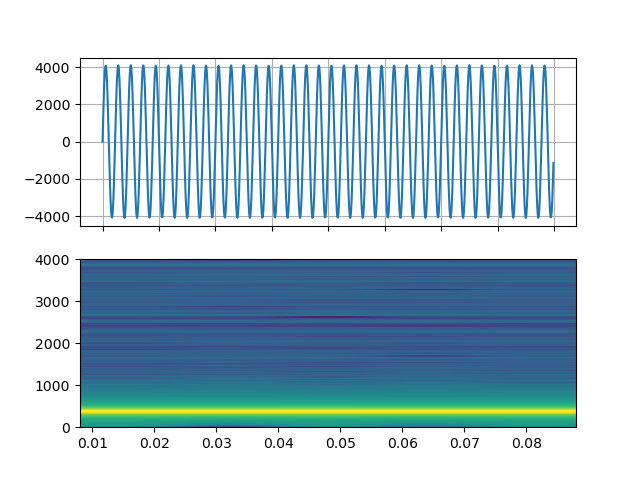
正弦波¶
https://ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg-filters.html#sine
StreamReader(src="sine=sample_rate=8000:frequency=360", format="lavfi")
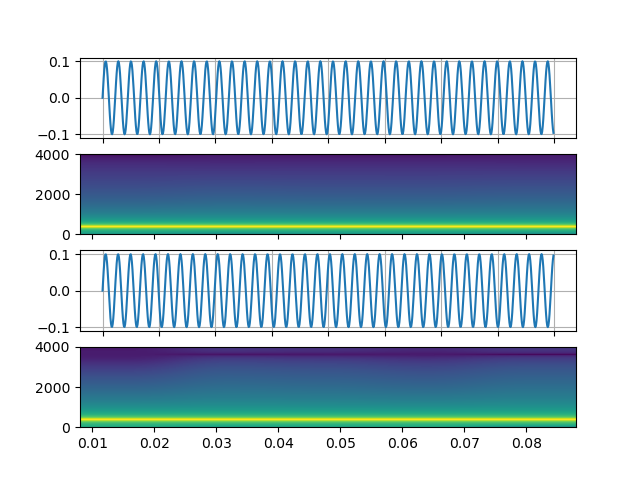
具有任意表达式的信号¶
https://ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg-filters.html#aevalsrc
# 5 Hz binaural beats on a 360 Hz carrier
StreamReader(
src=(
'aevalsrc='
'sample_rate=8000:'
'exprs=0.1*sin(2*PI*(360-5/2)*t)|0.1*sin(2*PI*(360+5/2)*t)'
),
format='lavfi',
)
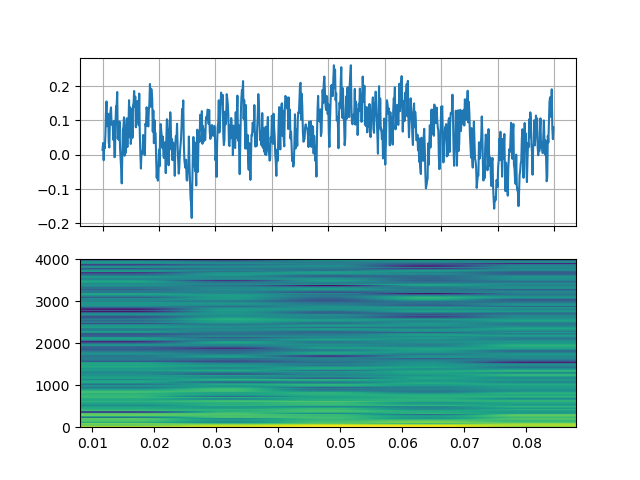
噪声¶
https://ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg-filters.html#anoisesrc
StreamReader(src="anoisesrc=color=pink:sample_rate=8000:amplitude=0.5", format="lavfi")
视频示例¶
元胞自动机¶
https://ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg-filters.html#cellauto
StreamReader(src=f"cellauto", format="lavfi")
曼德布洛特¶
https://ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg-filters.html#cellauto
StreamReader(src=f"mandelbrot", format="lavfi")
MPlayer 测试模式¶
https://ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg-filters.html#mptestsrc
StreamReader(src=f"mptestsrc", format="lavfi")
约翰·康威的人生游戏¶
https://ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg-filters.html#life
StreamReader(src=f"life", format="lavfi")
谢尔宾斯基地毯/三角形分形¶
https://ffmpeg.org/ffmpeg-filters.html#sierpinski
StreamReader(src=f"sierpinski", format="lavfi")
自定义过滤器¶
在定义输出流时,您可以使用 and 方法。add_audio_stream()add_video_stream()
这些方法接受 argument,它是一个字符串
根据 FFMPEG 的 Filter 表达式进行格式设置。filter_desc
和 之间的区别在于构造筛选表达式并将其传递给相同的底层
实现。一切都可以
通过 实现。add_basic_(audio|video)_streamadd_(audio|video)_streamadd_basic_(audio|video)_streamadd_basic_(audio|video)_streamadd_(audio|video)_stream
注意
应用自定义筛选条件时,客户端代码必须转换 音频/视频流为 TorchAudio 可以转换为 Tensor 格式。 例如,这可以通过应用于视频流和音频流来实现。
format=pix_fmts=rgb24aformat=sample_fmts=fltp每个输出流都有单独的筛选器图。因此,它是 不能对 filter 表达式。但是,可以拆分一个输入 流式传输到多个 Film,并在以后合并它们。
音频示例¶
# fmt: off
descs = [
# No filtering
"anull",
# Apply a highpass filter then a lowpass filter
"highpass=f=200,lowpass=f=1000",
# Manipulate spectrogram
(
"afftfilt="
"real='hypot(re,im)*sin(0)':"
"imag='hypot(re,im)*cos(0)':"
"win_size=512:"
"overlap=0.75"
),
# Manipulate spectrogram
(
"afftfilt="
"real='hypot(re,im)*cos((random(0)*2-1)*2*3.14)':"
"imag='hypot(re,im)*sin((random(1)*2-1)*2*3.14)':"
"win_size=128:"
"overlap=0.8"
),
]
# fmt: on
sample_rate = 8000
streamer = StreamReader(AUDIO_URL)
for desc in descs:
streamer.add_audio_stream(
frames_per_chunk=40000,
filter_desc=f"aresample={sample_rate},{desc},aformat=sample_fmts=fltp",
)
chunks = next(streamer.stream())
def _display(i):
print("filter_desc:", streamer.get_out_stream_info(i).filter_description)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1)
waveform = chunks[i][:, 0]
axs[0].plot(waveform)
axs[0].grid(True)
axs[0].set_ylim([-1, 1])
plt.setp(axs[0].get_xticklabels(), visible=False)
axs[1].specgram(waveform, Fs=sample_rate)
fig.tight_layout()
return IPython.display.Audio(chunks[i].T, rate=sample_rate)
源语言¶
_display(0)
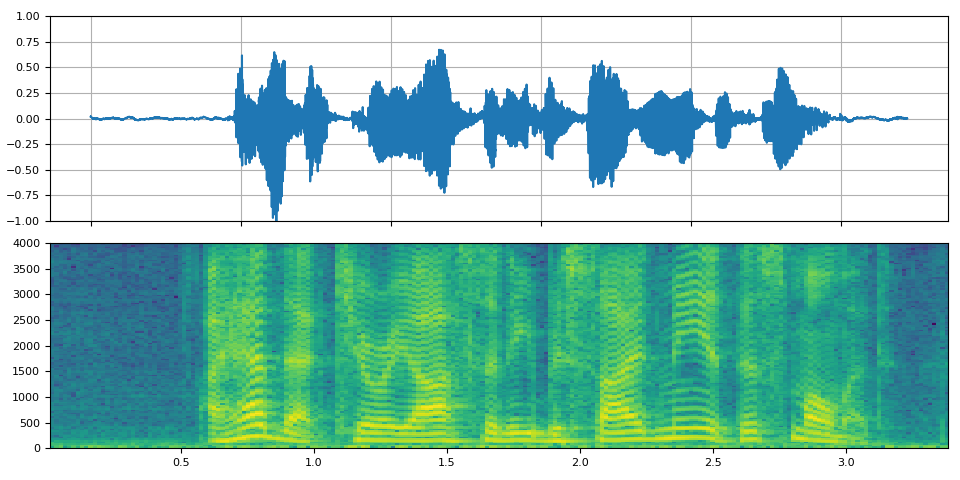
filter_desc: aresample=8000,anull,aformat=sample_fmts=fltp
高通/低通滤波器¶
_display(1)
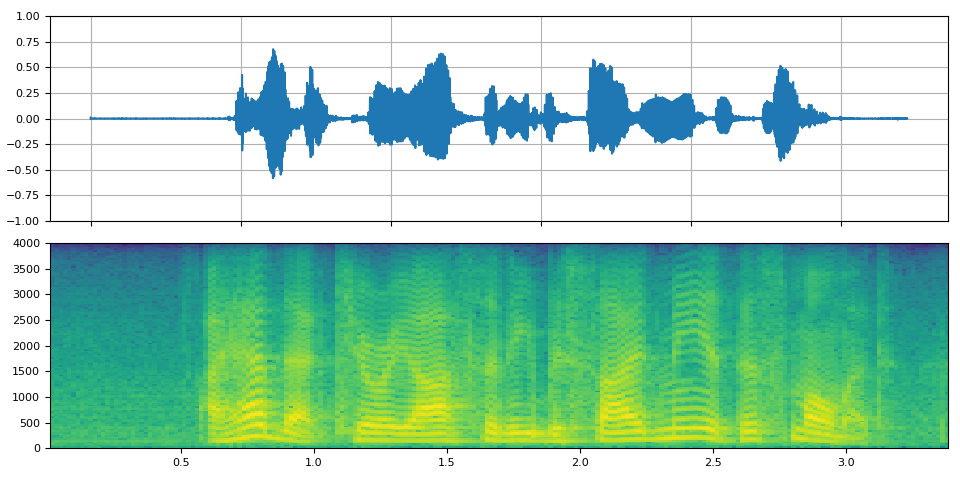
filter_desc: aresample=8000,highpass=f=200,lowpass=f=1000,aformat=sample_fmts=fltp
FFT 滤波器 - 机器人 🤖¶
_display(2)
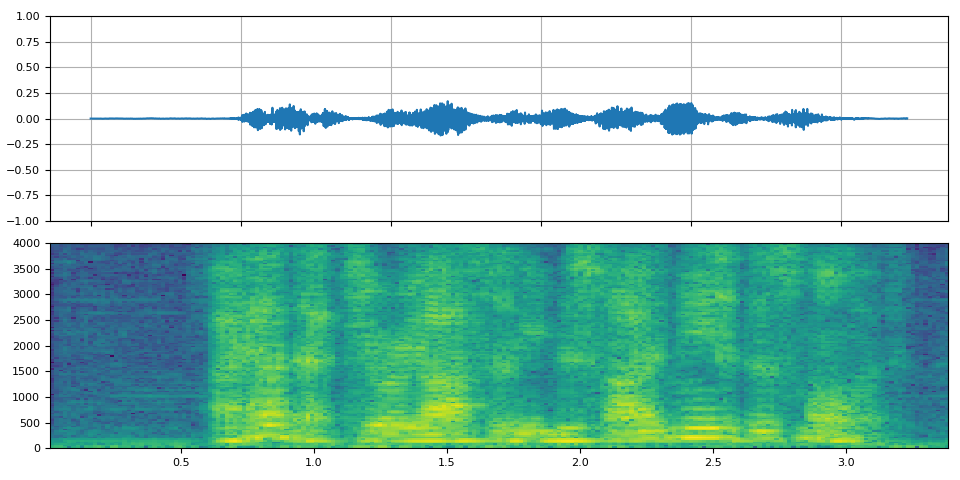
filter_desc: aresample=8000,afftfilt=real='hypot(re,im)*sin(0)':imag='hypot(re,im)*cos(0)':win_size=512:overlap=0.75,aformat=sample_fmts=fltp
FFT 滤波器 - Whisper¶
_display(3)
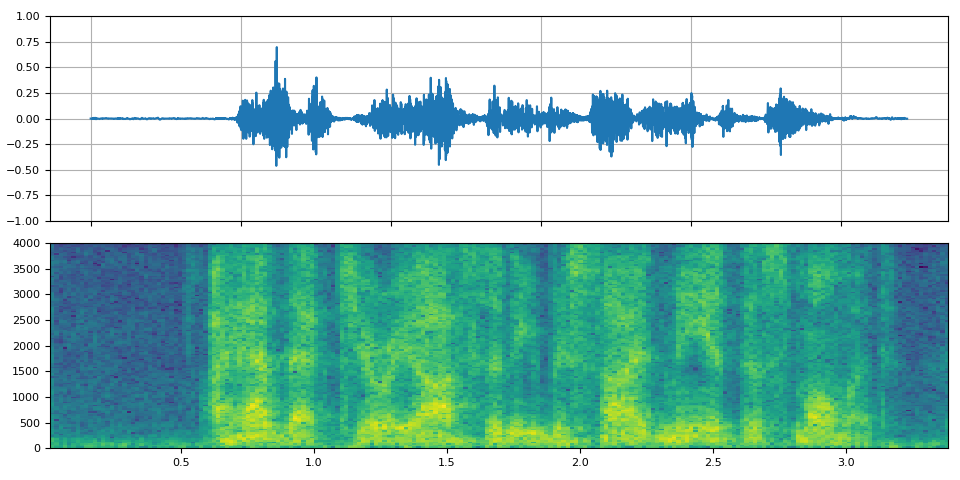
filter_desc: aresample=8000,afftfilt=real='hypot(re,im)*cos((random(0)*2-1)*2*3.14)':imag='hypot(re,im)*sin((random(1)*2-1)*2*3.14)':win_size=128:overlap=0.8,aformat=sample_fmts=fltp
视频示例¶
# fmt: off
descs = [
# No effect
"null",
# Split the input stream and apply horizontal flip to the right half.
(
"split [main][tmp];"
"[tmp] crop=iw/2:ih:0:0, hflip [flip];"
"[main][flip] overlay=W/2:0"
),
# Edge detection
"edgedetect=mode=canny",
# Rotate image by randomly and fill the background with brown
"rotate=angle=-random(1)*PI:fillcolor=brown",
# Manipulate pixel values based on the coordinate
"geq=r='X/W*r(X,Y)':g='(1-X/W)*g(X,Y)':b='(H-Y)/H*b(X,Y)'"
]
# fmt: on
streamer = StreamReader(VIDEO_URL)
for desc in descs:
streamer.add_video_stream(
frames_per_chunk=30,
filter_desc=f"fps=10,{desc},format=pix_fmts=rgb24",
)
streamer.seek(12)
chunks = next(streamer.stream())
def _display(i):
print("filter_desc:", streamer.get_out_stream_info(i).filter_description)
_, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(8, 1.9))
chunk = chunks[i]
for j in range(3):
axs[j].imshow(chunk[10 * j + 1].permute(1, 2, 0))
axs[j].set_axis_off()
plt.tight_layout()
源语言¶
_display(0)
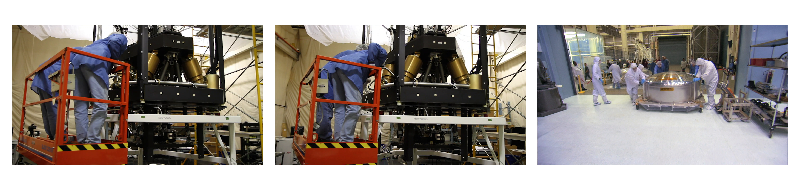
filter_desc: fps=10,null,format=pix_fmts=rgb24
镜子¶
_display(1)

filter_desc: fps=10,split [main][tmp];[tmp] crop=iw/2:ih:0:0, hflip [flip];[main][flip] overlay=W/2:0,format=pix_fmts=rgb24
边缘检测¶
_display(2)
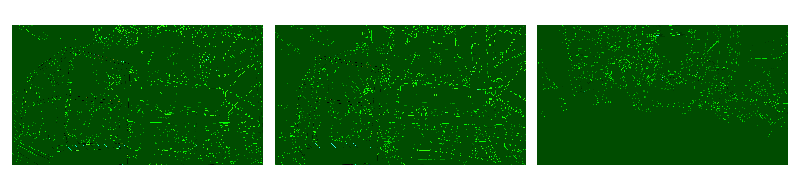
filter_desc: fps=10,edgedetect=mode=canny,format=pix_fmts=rgb24
随机旋转¶
_display(3)

filter_desc: fps=10,rotate=angle=-random(1)*PI:fillcolor=brown,format=pix_fmts=rgb24
像素作¶
_display(4)

filter_desc: fps=10,geq=r='X/W*r(X,Y)':g='(1-X/W)*g(X,Y)':b='(H-Y)/H*b(X,Y)',format=pix_fmts=rgb24
脚本总运行时间:(0 分 18.695 秒)