注意
转到最后下载完整的示例代码
导出到 ExecuTorch 教程¶
作者: Angela Yi
ExecuTorch 是一个统一的 ML 堆栈,用于将 PyTorch 模型降低到边缘设备。 它引入了改进的入口点来执行模型、设备和/或用例 特定优化,例如后端委托、用户定义的编译器 转换、默认或用户定义的内存规划等。
概括地说,工作流如下所示:
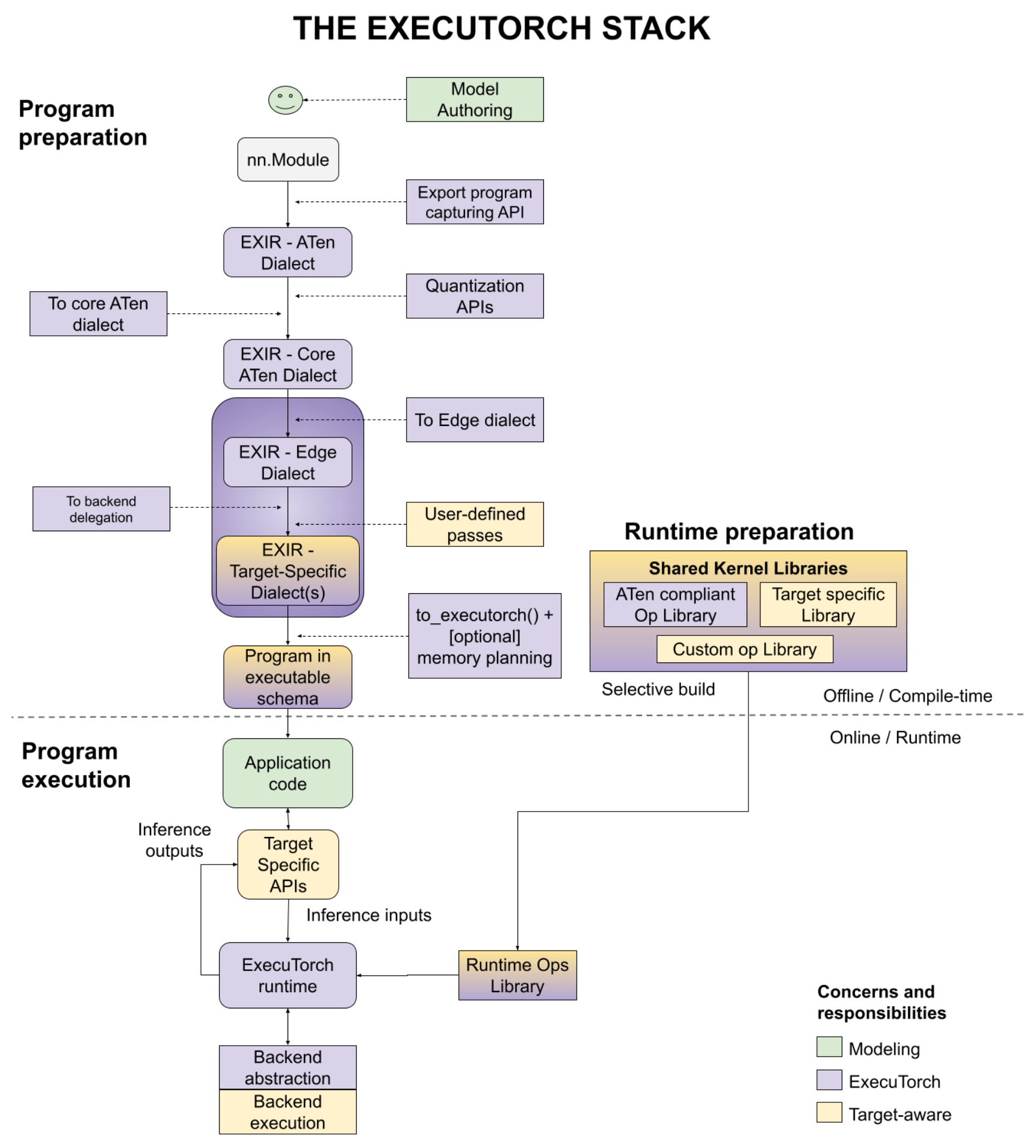
在本教程中,我们将介绍“程序准备”步骤中的 API,以 将 PyTorch 模型降低为可加载到设备并在 ExecuTorch 运行时。
先决条件¶
要运行本教程,您首先需要设置 ExecuTorch 环境。
导出模型¶
注意:Export API 仍在进行更改,以更好地与 长期出口状态。有关更多详细信息,请参阅此问题。
降级到 ExecuTorch 的第一步是将给定的模型(任何
callable 或 ) 转换为图形表示形式。这是通过 ,它接受一个 , 一个
positional arguments,也可以选择关键字参数的字典(未显示
)和动态形状列表(稍后介绍)。torch.nn.Moduletorch.exporttorch.nn.Module
import torch
from torch.export import export, ExportedProgram
class SimpleConv(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.conv = torch.nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=3, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, padding=1
)
self.relu = torch.nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
a = self.conv(x)
return self.relu(a)
example_args = (torch.randn(1, 3, 256, 256),)
aten_dialect: ExportedProgram = export(SimpleConv(), example_args)
print(aten_dialect)
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, p_conv_weight: "f32[16, 3, 3, 3]", p_conv_bias: "f32[16]", x: "f32[1, 3, 256, 256]"):
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:64 in forward, code: a = self.conv(x)
conv2d: "f32[1, 16, 256, 256]" = torch.ops.aten.conv2d.default(x, p_conv_weight, p_conv_bias, [1, 1], [1, 1]); x = p_conv_weight = p_conv_bias = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:65 in forward, code: return self.relu(a)
relu: "f32[1, 16, 256, 256]" = torch.ops.aten.relu.default(conv2d); conv2d = None
return (relu,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.PARAMETER: 2>, arg=TensorArgument(name='p_conv_weight'), target='conv.weight', persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.PARAMETER: 2>, arg=TensorArgument(name='p_conv_bias'), target='conv.bias', persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='relu'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
的输出是一个完全扁平化的图形(意味着
Graph 不包含任何 Module 层次结构,Control 除外
流运算符)。此外,该图是纯函数式的,这意味着它确实
不包含具有副作用(如突变或别名)的操作。torch.export.export
有关结果的更多规范,请参见 此处 .torch.export
返回的图形仅包含函数式 ATen 运算符
(~2000 次操作),我们将其称为 .torch.exportATen Dialect
表达活力¶
默认情况下,导出流将跟踪程序,假设所有输入 形状是静态的,因此如果我们使用具有以下 与我们在 tracing 时使用的 Settings 不同,我们将遇到一个错误:
import traceback as tb
class Basic(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, y: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
return x + y
example_args = (torch.randn(3, 3), torch.randn(3, 3))
aten_dialect: ExportedProgram = export(Basic(), example_args)
# Works correctly
print(aten_dialect.module()(torch.ones(3, 3), torch.ones(3, 3)))
# Errors
try:
print(aten_dialect.module()(torch.ones(3, 2), torch.ones(3, 2)))
except Exception:
tb.print_exc()
tensor([[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.]])
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py", line 111, in <module>
print(aten_dialect.module()(torch.ones(3, 2), torch.ones(3, 2)))
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/fx/graph_module.py", line 738, in call_wrapped
return self._wrapped_call(self, *args, **kwargs)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/fx/graph_module.py", line 316, in __call__
raise e
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/fx/graph_module.py", line 303, in __call__
return super(self.cls, obj).__call__(*args, **kwargs) # type: ignore[misc]
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1553, in _wrapped_call_impl
return self._call_impl(*args, **kwargs)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1582, in _call_impl
args_kwargs_result = hook(self, args, kwargs) # type: ignore[misc]
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/eval_frame.py", line 600, in _fn
return fn(*args, **kwargs)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/export/_unlift.py", line 33, in _check_input_constraints_pre_hook
return _check_input_constraints_for_graph(
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_export/utils.py", line 155, in _check_input_constraints_for_graph
raise RuntimeError(
RuntimeError: Expected input at *args[0].shape[1] to be equal to 3, but got 2
- 为了表示某些输入形状是动态的,我们可以插入动态
shapes 添加到导出流程中。这是通过 API 完成的:
Dim
from torch.export import Dim
class Basic(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, y: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
return x + y
example_args = (torch.randn(3, 3), torch.randn(3, 3))
dim1_x = Dim("dim1_x", min=1, max=10)
dynamic_shapes = {"x": {1: dim1_x}, "y": {1: dim1_x}}
aten_dialect: ExportedProgram = export(
Basic(), example_args, dynamic_shapes=dynamic_shapes
)
print(aten_dialect)
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, x: "f32[3, s0]", y: "f32[3, s0]"):
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:127 in forward, code: return x + y
add: "f32[3, s0]" = torch.ops.aten.add.Tensor(x, y); x = y = None
return (add,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='y'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='add'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {s0: VR[1, 10]}
请注意,输入 和 现在具有形状 (3, s0),
替换为一个符号,表示此维度可以是范围
的值。arg0_1arg1_1s0
此外,我们可以在 Range 约束中看到 value of 具有
范围 [1, 10],由我们的动态形状指定。s0
现在让我们尝试运行具有不同形状的模型:
# Works correctly
print(aten_dialect.module()(torch.ones(3, 3), torch.ones(3, 3)))
print(aten_dialect.module()(torch.ones(3, 2), torch.ones(3, 2)))
# Errors because it violates our constraint that input 0, dim 1 <= 10
try:
print(aten_dialect.module()(torch.ones(3, 15), torch.ones(3, 15)))
except Exception:
tb.print_exc()
# Errors because it violates our constraint that input 0, dim 1 == input 1, dim 1
try:
print(aten_dialect.module()(torch.ones(3, 3), torch.ones(3, 2)))
except Exception:
tb.print_exc()
tensor([[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.]])
tensor([[2., 2.],
[2., 2.],
[2., 2.]])
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py", line 154, in <module>
print(aten_dialect.module()(torch.ones(3, 15), torch.ones(3, 15)))
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/fx/graph_module.py", line 738, in call_wrapped
return self._wrapped_call(self, *args, **kwargs)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/fx/graph_module.py", line 316, in __call__
raise e
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/fx/graph_module.py", line 303, in __call__
return super(self.cls, obj).__call__(*args, **kwargs) # type: ignore[misc]
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1553, in _wrapped_call_impl
return self._call_impl(*args, **kwargs)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1582, in _call_impl
args_kwargs_result = hook(self, args, kwargs) # type: ignore[misc]
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/eval_frame.py", line 600, in _fn
return fn(*args, **kwargs)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/export/_unlift.py", line 33, in _check_input_constraints_pre_hook
return _check_input_constraints_for_graph(
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_export/utils.py", line 145, in _check_input_constraints_for_graph
raise RuntimeError(
RuntimeError: Expected input at *args[0].shape[1] to be <= 10, but got 15
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py", line 160, in <module>
print(aten_dialect.module()(torch.ones(3, 3), torch.ones(3, 2)))
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/fx/graph_module.py", line 738, in call_wrapped
return self._wrapped_call(self, *args, **kwargs)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/fx/graph_module.py", line 316, in __call__
raise e
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/fx/graph_module.py", line 303, in __call__
return super(self.cls, obj).__call__(*args, **kwargs) # type: ignore[misc]
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1553, in _wrapped_call_impl
return self._call_impl(*args, **kwargs)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py", line 1582, in _call_impl
args_kwargs_result = hook(self, args, kwargs) # type: ignore[misc]
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_dynamo/eval_frame.py", line 600, in _fn
return fn(*args, **kwargs)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/export/_unlift.py", line 33, in _check_input_constraints_pre_hook
return _check_input_constraints_for_graph(
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_export/utils.py", line 107, in _check_input_constraints_for_graph
raise RuntimeError(
RuntimeError: Expected input at *args[1].shape[1] to be equal to 3, but got 2
寻址无法追踪的代码¶
由于我们的目标是从 PyTorch 捕获整个计算图 程序中,我们最终可能会遇到程序中无法追踪的部分。自 解决这些问题,torch.export 文档, 或者 torch.export 教程将是最好的查看位置。
执行量化¶
要量化模型,我们首先需要使用 捕获图形,执行量化,然后
叫。 返回
graph 中包含 Autograd 安全的 ATen 运算符,这意味着它们是
safe 用于量化所需的 Eager Mode 训练。我们将调用
此级别的图形,即图形。torch._export.capture_pre_autograd_graphtorch.exporttorch._export.capture_pre_autograd_graphPre-Autograd ATen Dialect
与 FX Graph Mode 量化相比,
我们需要调用两个新的 API:and,而不是 和 。它的不同之处在于,它采用特定于后端的参数,该
将使用量化
model。prepare_pt2econvert_pt2eprepare_fxconvert_fxprepare_pt2eQuantizer
from torch._export import capture_pre_autograd_graph
example_args = (torch.randn(1, 3, 256, 256),)
pre_autograd_aten_dialect = capture_pre_autograd_graph(SimpleConv(), example_args)
print("Pre-Autograd ATen Dialect Graph")
print(pre_autograd_aten_dialect)
from torch.ao.quantization.quantize_pt2e import convert_pt2e, prepare_pt2e
from torch.ao.quantization.quantizer.xnnpack_quantizer import (
get_symmetric_quantization_config,
XNNPACKQuantizer,
)
quantizer = XNNPACKQuantizer().set_global(get_symmetric_quantization_config())
prepared_graph = prepare_pt2e(pre_autograd_aten_dialect, quantizer)
# calibrate with a sample dataset
converted_graph = convert_pt2e(prepared_graph)
print("Quantized Graph")
print(converted_graph)
aten_dialect: ExportedProgram = export(converted_graph, example_args)
print("ATen Dialect Graph")
print(aten_dialect)
Pre-Autograd ATen Dialect Graph
GraphModule()
def forward(self, x):
arg0, = fx_pytree.tree_flatten_spec(([x], {}), self._in_spec)
arg0_1 = arg0
_param_constant0 = self.conv_weight
_param_constant1 = self.conv_bias
conv2d = torch.ops.aten.conv2d.default(arg0_1, _param_constant0, _param_constant1, [1, 1], [1, 1]); arg0_1 = _param_constant0 = _param_constant1 = None
relu = torch.ops.aten.relu.default(conv2d); conv2d = None
return pytree.tree_unflatten([relu], self._out_spec)
# To see more debug info, please use `graph_module.print_readable()`
/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/ao/quantization/observer.py:1289: UserWarning: must run observer before calling calculate_qparams. Returning default scale and zero point
warnings.warn(
/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/ao/quantization/utils.py:376: UserWarning: must run observer before calling calculate_qparams. Returning default values.
warnings.warn(
Quantized Graph
GraphModule()
def forward(self, x):
arg0, = fx_pytree.tree_flatten_spec(([x], {}), self._in_spec)
arg0_1 = arg0
quantize_per_tensor_default = torch.ops.quantized_decomposed.quantize_per_tensor.default(arg0_1, 1.0, 0, -128, 127, torch.int8); arg0_1 = None
dequantize_per_tensor_default = torch.ops.quantized_decomposed.dequantize_per_tensor.default(quantize_per_tensor_default, 1.0, 0, -128, 127, torch.int8); quantize_per_tensor_default = None
_frozen_param0 = self._frozen_param0
dequantize_per_tensor_default_1 = torch.ops.quantized_decomposed.dequantize_per_tensor.default(_frozen_param0, 1.0, 0, -127, 127, torch.int8); _frozen_param0 = None
_param_constant1 = self.conv_bias
conv2d = torch.ops.aten.conv2d.default(dequantize_per_tensor_default, dequantize_per_tensor_default_1, _param_constant1, [1, 1], [1, 1]); dequantize_per_tensor_default = dequantize_per_tensor_default_1 = _param_constant1 = None
relu = torch.ops.aten.relu.default(conv2d); conv2d = None
quantize_per_tensor_default_2 = torch.ops.quantized_decomposed.quantize_per_tensor.default(relu, 1.0, 0, -128, 127, torch.int8); relu = None
dequantize_per_tensor_default_2 = torch.ops.quantized_decomposed.dequantize_per_tensor.default(quantize_per_tensor_default_2, 1.0, 0, -128, 127, torch.int8); quantize_per_tensor_default_2 = None
return pytree.tree_unflatten([dequantize_per_tensor_default_2], self._out_spec)
# To see more debug info, please use `graph_module.print_readable()`
/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_subclasses/functional_tensor.py:362: UserWarning: At pre-dispatch tracing, we will assume that any custom op that is marked with CompositeImplicitAutograd and functional are safe to not decompose. We found quantized_decomposed.quantize_per_tensor.default to be one such op.
warnings.warn(
/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/_subclasses/functional_tensor.py:362: UserWarning: At pre-dispatch tracing, we will assume that any custom op that is marked with CompositeImplicitAutograd and functional are safe to not decompose. We found quantized_decomposed.dequantize_per_tensor.default to be one such op.
warnings.warn(
ATen Dialect Graph
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, p_conv_bias: "f32[16]", b__frozen_param0: "i8[16, 3, 3, 3]", x: "f32[1, 3, 256, 256]"):
# File: <eval_with_key>.169:7 in forward, code: quantize_per_tensor_default = torch.ops.quantized_decomposed.quantize_per_tensor.default(arg0_1, 1.0, 0, -128, 127, torch.int8); arg0_1 = None
quantize_per_tensor: "i8[1, 3, 256, 256]" = torch.ops.quantized_decomposed.quantize_per_tensor.default(x, 1.0, 0, -128, 127, torch.int8); x = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:64 in forward, code: a = self.conv(x)
dequantize_per_tensor: "f32[1, 3, 256, 256]" = torch.ops.quantized_decomposed.dequantize_per_tensor.default(quantize_per_tensor, 1.0, 0, -128, 127, torch.int8); quantize_per_tensor = None
dequantize_per_tensor_1: "f32[16, 3, 3, 3]" = torch.ops.quantized_decomposed.dequantize_per_tensor.default(b__frozen_param0, 1.0, 0, -127, 127, torch.int8); b__frozen_param0 = None
conv2d: "f32[1, 16, 256, 256]" = torch.ops.aten.conv2d.default(dequantize_per_tensor, dequantize_per_tensor_1, p_conv_bias, [1, 1], [1, 1]); dequantize_per_tensor = dequantize_per_tensor_1 = p_conv_bias = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:65 in forward, code: return self.relu(a)
relu: "f32[1, 16, 256, 256]" = torch.ops.aten.relu.default(conv2d); conv2d = None
quantize_per_tensor_1: "i8[1, 16, 256, 256]" = torch.ops.quantized_decomposed.quantize_per_tensor.default(relu, 1.0, 0, -128, 127, torch.int8); relu = None
# File: <eval_with_key>.169:15 in forward, code: dequantize_per_tensor_default_2 = torch.ops.quantized_decomposed.dequantize_per_tensor.default(quantize_per_tensor_default_2, 1.0, 0, -128, 127, torch.int8); quantize_per_tensor_default_2 = None
dequantize_per_tensor_2: "f32[1, 16, 256, 256]" = torch.ops.quantized_decomposed.dequantize_per_tensor.default(quantize_per_tensor_1, 1.0, 0, -128, 127, torch.int8); quantize_per_tensor_1 = None
return (dequantize_per_tensor_2,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.PARAMETER: 2>, arg=TensorArgument(name='p_conv_bias'), target='conv_bias', persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.BUFFER: 3>, arg=TensorArgument(name='b__frozen_param0'), target='_frozen_param0', persistent=True), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='dequantize_per_tensor_2'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
有关如何量化模型以及后端如何实现 的更多信息,请参见 此处.Quantizer
降低到 Edge Dialect¶
导出图表并将其降低到 后,下一步
是降低到 ,其中有用的特化
对于边缘设备,但对于一般(服务器)环境不是必需的
应用的。
其中一些专业包括:ATen DialectEdge Dialect
DType 专业化
标量到张量的转换
将所有操作转换为命名空间。
executorch.exir.dialects.edge
请注意,此方言仍然与后端(或目标)无关。
降低是通过 API 完成的。to_edge
from executorch.exir import EdgeProgramManager, to_edge
example_args = (torch.randn(1, 3, 256, 256),)
aten_dialect: ExportedProgram = export(SimpleConv(), example_args)
edge_program: EdgeProgramManager = to_edge(aten_dialect)
print("Edge Dialect Graph")
print(edge_program.exported_program())
Edge Dialect Graph
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, p_conv_weight: "f32[16, 3, 3, 3]", p_conv_bias: "f32[16]", x: "f32[1, 3, 256, 256]"):
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:64 in forward, code: a = self.conv(x)
aten_convolution_default: "f32[1, 16, 256, 256]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_convolution_default(x, p_conv_weight, p_conv_bias, [1, 1], [1, 1], [1, 1], False, [0, 0], 1); x = p_conv_weight = p_conv_bias = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:65 in forward, code: return self.relu(a)
aten_relu_default: "f32[1, 16, 256, 256]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_relu_default(aten_convolution_default); aten_convolution_default = None
return (aten_relu_default,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.PARAMETER: 2>, arg=TensorArgument(name='p_conv_weight'), target='conv.weight', persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.PARAMETER: 2>, arg=TensorArgument(name='p_conv_bias'), target='conv.bias', persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_relu_default'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
to_edge()返回一个对象,其中包含
导出的程序,这些程序将被放置在此设备上。此数据结构
允许用户导出多个程序并将它们合并为一个二进制文件。如果
只有一个程序,默认情况下,它将保存为“forward”名称。EdgeProgramManager
class Encode(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return torch.nn.functional.linear(x, torch.randn(5, 10))
class Decode(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return torch.nn.functional.linear(x, torch.randn(10, 5))
encode_args = (torch.randn(1, 10),)
aten_encode: ExportedProgram = export(Encode(), encode_args)
decode_args = (torch.randn(1, 5),)
aten_decode: ExportedProgram = export(Decode(), decode_args)
edge_program: EdgeProgramManager = to_edge(
{"encode": aten_encode, "decode": aten_decode}
)
for method in edge_program.methods:
print(f"Edge Dialect graph of {method}")
print(edge_program.exported_program(method))
Edge Dialect graph of encode
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, x: "f32[1, 10]"):
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:261 in forward, code: return torch.nn.functional.linear(x, torch.randn(5, 10))
aten_randn_default: "f32[5, 10]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_randn_default([5, 10], device = device(type='cpu'), pin_memory = False)
aten_permute_copy_default: "f32[10, 5]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_permute_copy_default(aten_randn_default, [1, 0]); aten_randn_default = None
aten_mm_default: "f32[1, 5]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_mm_default(x, aten_permute_copy_default); x = aten_permute_copy_default = None
return (aten_mm_default,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_mm_default'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
Edge Dialect graph of decode
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, x: "f32[1, 5]"):
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:266 in forward, code: return torch.nn.functional.linear(x, torch.randn(10, 5))
aten_randn_default: "f32[10, 5]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_randn_default([10, 5], device = device(type='cpu'), pin_memory = False)
aten_permute_copy_default: "f32[5, 10]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_permute_copy_default(aten_randn_default, [1, 0]); aten_randn_default = None
aten_mm_default: "f32[1, 10]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_mm_default(x, aten_permute_copy_default); x = aten_permute_copy_default = None
return (aten_mm_default,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_mm_default'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
我们还可以通过
API 的 API 创建。有关如何编写的深入文档
可在此处找到转换。transform
请注意,由于图形现在位于 Edge Dialect 中,因此所有通道也必须
生成有效的 Edge Dialect 图(具体需要指出的一点是
运算符现在位于命名空间中,
而不是命名空间。executorch.exir.dialects.edgetorch.ops.aten
example_args = (torch.randn(1, 3, 256, 256),)
aten_dialect: ExportedProgram = export(SimpleConv(), example_args)
edge_program: EdgeProgramManager = to_edge(aten_dialect)
print("Edge Dialect Graph")
print(edge_program.exported_program())
from executorch.exir.dialects._ops import ops as exir_ops
from executorch.exir.pass_base import ExportPass
class ConvertReluToSigmoid(ExportPass):
def call_operator(self, op, args, kwargs, meta):
if op == exir_ops.edge.aten.relu.default:
return super().call_operator(
exir_ops.edge.aten.sigmoid.default, args, kwargs, meta
)
else:
return super().call_operator(op, args, kwargs, meta)
transformed_edge_program = edge_program.transform((ConvertReluToSigmoid(),))
print("Transformed Edge Dialect Graph")
print(transformed_edge_program.exported_program())
Edge Dialect Graph
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, p_conv_weight: "f32[16, 3, 3, 3]", p_conv_bias: "f32[16]", x: "f32[1, 3, 256, 256]"):
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:64 in forward, code: a = self.conv(x)
aten_convolution_default: "f32[1, 16, 256, 256]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_convolution_default(x, p_conv_weight, p_conv_bias, [1, 1], [1, 1], [1, 1], False, [0, 0], 1); x = p_conv_weight = p_conv_bias = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:65 in forward, code: return self.relu(a)
aten_relu_default: "f32[1, 16, 256, 256]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_relu_default(aten_convolution_default); aten_convolution_default = None
return (aten_relu_default,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.PARAMETER: 2>, arg=TensorArgument(name='p_conv_weight'), target='conv.weight', persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.PARAMETER: 2>, arg=TensorArgument(name='p_conv_bias'), target='conv.bias', persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_relu_default'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
Transformed Edge Dialect Graph
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, p_conv_weight: "f32[16, 3, 3, 3]", p_conv_bias: "f32[16]", x: "f32[1, 3, 256, 256]"):
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:64 in forward, code: a = self.conv(x)
aten_convolution_default: "f32[1, 16, 256, 256]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_convolution_default(x, p_conv_weight, p_conv_bias, [1, 1], [1, 1], [1, 1], False, [0, 0], 1); x = p_conv_weight = p_conv_bias = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:65 in forward, code: return self.relu(a)
aten_sigmoid_default: "f32[1, 16, 256, 256]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_sigmoid_default(aten_convolution_default); aten_convolution_default = None
return (aten_sigmoid_default,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.PARAMETER: 2>, arg=TensorArgument(name='p_conv_weight'), target='conv.weight', persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.PARAMETER: 2>, arg=TensorArgument(name='p_conv_bias'), target='conv.bias', persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_sigmoid_default'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
注意:如果您看到类似 ,
请在 https://github.com/pytorch/executorch/issues 中提交问题,我们很乐意提供帮助!torch._export.verifier.SpecViolationError:
Operator torch._ops.aten._native_batch_norm_legit_functional.default is not
Aten Canonical
委托给后端¶
现在,我们可以将图形的一部分或整个图形委托给第三方
backend 的 API 进行验证。有关
后端委托的细节,包括如何委托给后端和
如何实现后端,可以在这里找到。to_backend
有三种方法可以使用此 API:
我们可以降低整个模块。
我们可以将降低的模块插入到另一个更大的模块中。
我们可以将模块划分为可降低的子图,然后 将这些子图降低到后端。
降低整个模块¶
要降低整个模块,我们可以将后端名称
模块,以及一个编译规范列表,以帮助后端使用
降低过程。to_backend
class LowerableModule(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return torch.sin(x)
# Export and lower the module to Edge Dialect
example_args = (torch.ones(1),)
aten_dialect: ExportedProgram = export(LowerableModule(), example_args)
edge_program: EdgeProgramManager = to_edge(aten_dialect)
to_be_lowered_module = edge_program.exported_program()
from executorch.exir.backend.backend_api import LoweredBackendModule, to_backend
# Import the backend
from executorch.exir.backend.test.backend_with_compiler_demo import ( # noqa
BackendWithCompilerDemo,
)
# Lower the module
lowered_module: LoweredBackendModule = to_backend(
"BackendWithCompilerDemo", to_be_lowered_module, []
)
print(lowered_module)
print(lowered_module.backend_id)
print(lowered_module.processed_bytes)
print(lowered_module.original_module)
# Serialize and save it to a file
save_path = "delegate.pte"
with open(save_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(lowered_module.buffer())
LoweredBackendModule()
BackendWithCompilerDemo
b'1#op:demo::aten.sin.default, numel:1, dtype:torch.float32<debug_handle>1#'
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, x: "f32[1]"):
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:355 in forward, code: return torch.sin(x)
aten_sin_default: "f32[1]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_sin_default(x); x = None
return (aten_sin_default,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_sin_default'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
在此调用中,将返回一个 .一些
的重要属性包括:to_backendLoweredBackendModuleLoweredBackendModule
backend_id:此降低的模块将在 中运行的后端的名称 运行时processed_bytes:一个二进制 blob,它将告诉后端如何运行 运行时中的此程序original_module:原始导出的模块
将降低的模块组合成另一个模块¶
如果我们想在多个程序中重用这个降低的模块,我们 可以将这个降低的模块与另一个模块组合在一起。
class NotLowerableModule(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bias):
super().__init__()
self.bias = bias
def forward(self, a, b):
return torch.add(torch.add(a, b), self.bias)
class ComposedModule(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.non_lowerable = NotLowerableModule(torch.ones(1) * 0.3)
self.lowerable = lowered_module
def forward(self, x):
a = self.lowerable(x)
b = self.lowerable(a)
ret = self.non_lowerable(a, b)
return a, b, ret
example_args = (torch.ones(1),)
aten_dialect: ExportedProgram = export(ComposedModule(), example_args)
edge_program: EdgeProgramManager = to_edge(aten_dialect)
exported_program = edge_program.exported_program()
print("Edge Dialect graph")
print(exported_program)
print("Lowered Module within the graph")
print(exported_program.graph_module.lowered_module_0.backend_id)
print(exported_program.graph_module.lowered_module_0.processed_bytes)
print(exported_program.graph_module.lowered_module_0.original_module)
Edge Dialect graph
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, c_non_lowerable_bias: "f32[1]", x: "f32[1]"):
# File: /opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/executorch/exir/lowered_backend_module.py:337 in forward, code: return executorch_call_delegate(self, *args)
lowered_module_0 = self.lowered_module_0
executorch_call_delegate: "f32[1]" = torch.ops.higher_order.executorch_call_delegate(lowered_module_0, x); lowered_module_0 = x = None
# File: /opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/executorch/exir/lowered_backend_module.py:337 in forward, code: return executorch_call_delegate(self, *args)
lowered_module_1 = self.lowered_module_0
executorch_call_delegate_1: "f32[1]" = torch.ops.higher_order.executorch_call_delegate(lowered_module_1, executorch_call_delegate); lowered_module_1 = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:409 in forward, code: return torch.add(torch.add(a, b), self.bias)
aten_add_tensor: "f32[1]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_add_Tensor(executorch_call_delegate, executorch_call_delegate_1)
aten_add_tensor_1: "f32[1]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_add_Tensor(aten_add_tensor, c_non_lowerable_bias); aten_add_tensor = c_non_lowerable_bias = None
return (executorch_call_delegate, executorch_call_delegate_1, aten_add_tensor_1)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.CONSTANT_TENSOR: 4>, arg=TensorArgument(name='c_non_lowerable_bias'), target='non_lowerable.bias', persistent=True), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='executorch_call_delegate'), target=None), OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='executorch_call_delegate_1'), target=None), OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_add_tensor_1'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
Lowered Module within the graph
BackendWithCompilerDemo
b'1#op:demo::aten.sin.default, numel:1, dtype:torch.float32<debug_handle>1#'
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, x: "f32[1]"):
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:355 in forward, code: return torch.sin(x)
aten_sin_default: "f32[1]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_sin_default(x); x = None
return (aten_sin_default,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_sin_default'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
请注意,现在
graph 调用。此外,其内容与我们创建的相同
以前。torch.ops.higher_order.executorch_call_delegatelowered_module_0lowered_module_0lowered_module
模块的分区和下部¶
一个单独的下降流是将我们想要的模块
lower 和特定于后端的分区程序。 将使用
特定于后端的分区器来标记模块中可降低的节点,
将这些节点划分为子图,然后为每个子图创建一个。to_backendto_backendLoweredBackendModule
class Foo(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, a, x, b):
y = torch.mm(a, x)
z = y + b
a = z - a
y = torch.mm(a, x)
z = y + b
return z
example_args = (torch.randn(2, 2), torch.randn(2, 2), torch.randn(2, 2))
aten_dialect: ExportedProgram = export(Foo(), example_args)
edge_program: EdgeProgramManager = to_edge(aten_dialect)
exported_program = edge_program.exported_program()
print("Edge Dialect graph")
print(exported_program)
from executorch.exir.backend.test.op_partitioner_demo import AddMulPartitionerDemo
delegated_program = to_backend(exported_program, AddMulPartitionerDemo())
print("Delegated program")
print(delegated_program)
print(delegated_program.graph_module.lowered_module_0.original_module)
print(delegated_program.graph_module.lowered_module_1.original_module)
Edge Dialect graph
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, a: "f32[2, 2]", x: "f32[2, 2]", b: "f32[2, 2]"):
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:455 in forward, code: y = torch.mm(a, x)
aten_mm_default: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_mm_default(a, x)
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:456 in forward, code: z = y + b
aten_add_tensor: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_add_Tensor(aten_mm_default, b); aten_mm_default = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:457 in forward, code: a = z - a
aten_sub_tensor: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_sub_Tensor(aten_add_tensor, a); aten_add_tensor = a = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:458 in forward, code: y = torch.mm(a, x)
aten_mm_default_1: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_mm_default(aten_sub_tensor, x); aten_sub_tensor = x = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:459 in forward, code: z = y + b
aten_add_tensor_1: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_add_Tensor(aten_mm_default_1, b); aten_mm_default_1 = b = None
return (aten_add_tensor_1,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='a'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='b'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_add_tensor_1'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
Delegated program
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, a: "f32[2, 2]", x: "f32[2, 2]", b: "f32[2, 2]"):
# No stacktrace found for following nodes
lowered_module_0 = self.lowered_module_0
executorch_call_delegate = torch.ops.higher_order.executorch_call_delegate(lowered_module_0, a, x, b); lowered_module_0 = None
getitem: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_call_delegate[0]; executorch_call_delegate = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:457 in forward, code: a = z - a
aten_sub_tensor: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_sub_Tensor(getitem, a); getitem = a = None
# No stacktrace found for following nodes
lowered_module_1 = self.lowered_module_1
executorch_call_delegate_1 = torch.ops.higher_order.executorch_call_delegate(lowered_module_1, aten_sub_tensor, x, b); lowered_module_1 = aten_sub_tensor = x = b = None
getitem_1: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_call_delegate_1[0]; executorch_call_delegate_1 = None
return (getitem_1,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='a'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='b'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='getitem_1'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, a: "f32[2, 2]", x: "f32[2, 2]", b: "f32[2, 2]"):
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:455 in forward, code: y = torch.mm(a, x)
aten_mm_default: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_mm_default(a, x); a = x = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:456 in forward, code: z = y + b
aten_add_tensor: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_add_Tensor(aten_mm_default, b); aten_mm_default = b = None
return (aten_add_tensor,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='a'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='b'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_add_tensor'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, aten_sub_tensor: "f32[2, 2]", x: "f32[2, 2]", b: "f32[2, 2]"):
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:458 in forward, code: y = torch.mm(a, x)
aten_mm_default_1: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_mm_default(aten_sub_tensor, x); aten_sub_tensor = x = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:459 in forward, code: z = y + b
aten_add_tensor_1: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_add_Tensor(aten_mm_default_1, b); aten_mm_default_1 = b = None
return (aten_add_tensor_1,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_sub_tensor'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='b'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_add_tensor_1'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
请注意,现在
graph 中,一个包含操作 add、mul,另一个包含
操作 mul, add.torch.ops.higher_order.executorch_call_delegate
或者,一个更内聚的 API 来降低模块的下部部分是 directly
调用 IT:to_backend
class Foo(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, a, x, b):
y = torch.mm(a, x)
z = y + b
a = z - a
y = torch.mm(a, x)
z = y + b
return z
example_args = (torch.randn(2, 2), torch.randn(2, 2), torch.randn(2, 2))
aten_dialect: ExportedProgram = export(Foo(), example_args)
edge_program: EdgeProgramManager = to_edge(aten_dialect)
exported_program = edge_program.exported_program()
delegated_program = edge_program.to_backend(AddMulPartitionerDemo())
print("Delegated program")
print(delegated_program.exported_program())
Delegated program
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, a: "f32[2, 2]", x: "f32[2, 2]", b: "f32[2, 2]"):
# No stacktrace found for following nodes
lowered_module_0 = self.lowered_module_0
executorch_call_delegate = torch.ops.higher_order.executorch_call_delegate(lowered_module_0, a, x, b); lowered_module_0 = None
getitem: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_call_delegate[0]; executorch_call_delegate = None
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:491 in forward, code: a = z - a
aten_sub_tensor: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_dialects_edge__ops_aten_sub_Tensor(getitem, a); getitem = a = None
# No stacktrace found for following nodes
lowered_module_1 = self.lowered_module_1
executorch_call_delegate_1 = torch.ops.higher_order.executorch_call_delegate(lowered_module_1, aten_sub_tensor, x, b); lowered_module_1 = aten_sub_tensor = x = b = None
getitem_1: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_call_delegate_1[0]; executorch_call_delegate_1 = None
return (getitem_1,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='a'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='b'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='getitem_1'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
运行 User-Defined 走路和内存规划¶
作为降低 API 的最后一步,我们可以使用 API 传入
特定于后端的传递,例如将运算符集替换为自定义
backend 运算符和内存规划 pass 来告诉运行时如何
在运行程序时提前分配内存。to_executorch()
提供了默认的内存规划过程,但我们也可以选择一个 特定于后端的内存规划通过(如果存在)。更多信息 可在此处找到编写自定义内存规划过程
from executorch.exir import ExecutorchBackendConfig, ExecutorchProgramManager
from executorch.exir.passes import MemoryPlanningPass
executorch_program: ExecutorchProgramManager = edge_program.to_executorch(
ExecutorchBackendConfig(
passes=[], # User-defined passes
memory_planning_pass=MemoryPlanningPass(
"greedy"
), # Default memory planning pass
)
)
print("ExecuTorch Dialect")
print(executorch_program.exported_program())
import executorch.exir as exir
ExecuTorch Dialect
ExportedProgram:
class GraphModule(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, a: "f32[2, 2]", x: "f32[2, 2]", b: "f32[2, 2]"):
# No stacktrace found for following nodes
alloc: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_memory_alloc(((2, 2), torch.float32))
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:489 in forward, code: y = torch.mm(a, x)
aten_mm_default: "f32[2, 2]" = torch.ops.aten.mm.out(a, x, out = alloc); alloc = None
# No stacktrace found for following nodes
alloc_1: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_memory_alloc(((2, 2), torch.float32))
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:490 in forward, code: z = y + b
aten_add_tensor: "f32[2, 2]" = torch.ops.aten.add.out(aten_mm_default, b, out = alloc_1); aten_mm_default = alloc_1 = None
# No stacktrace found for following nodes
alloc_2: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_memory_alloc(((2, 2), torch.float32))
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:491 in forward, code: a = z - a
aten_sub_tensor: "f32[2, 2]" = torch.ops.aten.sub.out(aten_add_tensor, a, out = alloc_2); aten_add_tensor = a = alloc_2 = None
# No stacktrace found for following nodes
alloc_3: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_memory_alloc(((2, 2), torch.float32))
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:492 in forward, code: y = torch.mm(a, x)
aten_mm_default_1: "f32[2, 2]" = torch.ops.aten.mm.out(aten_sub_tensor, x, out = alloc_3); aten_sub_tensor = x = alloc_3 = None
# No stacktrace found for following nodes
alloc_4: "f32[2, 2]" = executorch_exir_memory_alloc(((2, 2), torch.float32))
# File: /pytorch/executorch/docs/source/tutorials_source/export-to-executorch-tutorial.py:493 in forward, code: z = y + b
aten_add_tensor_1: "f32[2, 2]" = torch.ops.aten.add.out(aten_mm_default_1, b, out = alloc_4); aten_mm_default_1 = b = alloc_4 = None
return (aten_add_tensor_1,)
Graph signature: ExportGraphSignature(input_specs=[InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='a'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='x'), target=None, persistent=None), InputSpec(kind=<InputKind.USER_INPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='b'), target=None, persistent=None)], output_specs=[OutputSpec(kind=<OutputKind.USER_OUTPUT: 1>, arg=TensorArgument(name='aten_add_tensor_1'), target=None)])
Range constraints: {}
请注意,在图形中,我们现在看到的是类似 and 而不是 and 的运算符。torch.ops.aten.sub.outtorch.ops.aten.div.outtorch.ops.aten.sub.Tensortorch.ops.aten.div.Tensor
这是因为在运行后端传递和内存规划传递之间,
为了准备图形以进行内存规划,在
将所有运算符转换为其 Out 变体的图表。而不是
在内核实现中分配返回的张量,运算符的变体将采用预同种异体化的张量到其输出的 kwarg,并且
将结果存储在那里,使内存规划者更容易执行 Tensor
寿命分析。out
我们还将节点插入到包含对特殊运算符的调用的图中。这告诉我们内存量是多少
需要分配 out-variant 运算符输出的每个张量。allocexecutorch.exir.memory.alloc
保存到文件¶
最后,我们可以将 ExecuTorch 程序保存到文件中,并将其加载到设备上 运行。
以下是整个端到端工作流的示例:
import torch
from torch._export import capture_pre_autograd_graph
from torch.export import export, ExportedProgram
class M(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.param = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.rand(3, 4))
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(4, 5)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x + self.param).clamp(min=0.0, max=1.0)
example_args = (torch.randn(3, 4),)
pre_autograd_aten_dialect = capture_pre_autograd_graph(M(), example_args)
# Optionally do quantization:
# pre_autograd_aten_dialect = convert_pt2e(prepare_pt2e(pre_autograd_aten_dialect, CustomBackendQuantizer))
aten_dialect: ExportedProgram = export(pre_autograd_aten_dialect, example_args)
edge_program: exir.EdgeProgramManager = exir.to_edge(aten_dialect)
# Optionally do delegation:
# edge_program = edge_program.to_backend(CustomBackendPartitioner)
executorch_program: exir.ExecutorchProgramManager = edge_program.to_executorch(
ExecutorchBackendConfig(
passes=[], # User-defined passes
)
)
with open("model.pte", "wb") as file:
file.write(executorch_program.buffer)