注意
单击此处下载完整的示例代码
音频特征提取¶
torchaudio实现音频中常用的特征提取
域。它们在 和 中可用。torchaudio.functionaltorchaudio.transforms
functional将功能实现为独立函数。
他们是无国籍的。
transforms将功能实现为对象,
using implementations from 和 .因为所有
转换是 的子类,它们可以被序列化
使用 TorchScript。functionaltorch.nn.Moduletorch.nn.Module
有关可用功能的完整列表,请参阅
文档。在本教程中,我们将研究在
时域和频域 (, , )。SpectrogramGriffinLimMelSpectrogram
# When running this tutorial in Google Colab, install the required packages
# with the following.
# !pip install torchaudio librosa
import torch
import torchaudio
import torchaudio.functional as F
import torchaudio.transforms as T
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
外:
1.11.0+cpu
0.11.0+cpu
准备数据和实用程序函数(跳过本节)¶
# @title Prepare data and utility functions. {display-mode: "form"}
# @markdown
# @markdown You do not need to look into this cell.
# @markdown Just execute once and you are good to go.
# @markdown
# @markdown In this tutorial, we will use a speech data from [VOiCES dataset](https://iqtlabs.github.io/voices/),
# @markdown which is licensed under Creative Commos BY 4.0.
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Preparation of data and helper functions.
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import os
import librosa
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import requests
from IPython.display import Audio, display
_SAMPLE_DIR = "_assets"
SAMPLE_WAV_SPEECH_URL = "https://pytorch-tutorial-assets.s3.amazonaws.com/VOiCES_devkit/source-16k/train/sp0307/Lab41-SRI-VOiCES-src-sp0307-ch127535-sg0042.wav" # noqa: E501
SAMPLE_WAV_SPEECH_PATH = os.path.join(_SAMPLE_DIR, "speech.wav")
os.makedirs(_SAMPLE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
def _fetch_data():
uri = [
(SAMPLE_WAV_SPEECH_URL, SAMPLE_WAV_SPEECH_PATH),
]
for url, path in uri:
with open(path, "wb") as file_:
file_.write(requests.get(url).content)
_fetch_data()
def _get_sample(path, resample=None):
effects = [["remix", "1"]]
if resample:
effects.extend(
[
["lowpass", f"{resample // 2}"],
["rate", f"{resample}"],
]
)
return torchaudio.sox_effects.apply_effects_file(path, effects=effects)
def get_speech_sample(*, resample=None):
return _get_sample(SAMPLE_WAV_SPEECH_PATH, resample=resample)
def print_stats(waveform, sample_rate=None, src=None):
if src:
print("-" * 10)
print("Source:", src)
print("-" * 10)
if sample_rate:
print("Sample Rate:", sample_rate)
print("Shape:", tuple(waveform.shape))
print("Dtype:", waveform.dtype)
print(f" - Max: {waveform.max().item():6.3f}")
print(f" - Min: {waveform.min().item():6.3f}")
print(f" - Mean: {waveform.mean().item():6.3f}")
print(f" - Std Dev: {waveform.std().item():6.3f}")
print()
print(waveform)
print()
def plot_spectrogram(spec, title=None, ylabel="freq_bin", aspect="auto", xmax=None):
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 1)
axs.set_title(title or "Spectrogram (db)")
axs.set_ylabel(ylabel)
axs.set_xlabel("frame")
im = axs.imshow(librosa.power_to_db(spec), origin="lower", aspect=aspect)
if xmax:
axs.set_xlim((0, xmax))
fig.colorbar(im, ax=axs)
plt.show(block=False)
def plot_waveform(waveform, sample_rate, title="Waveform", xlim=None, ylim=None):
waveform = waveform.numpy()
num_channels, num_frames = waveform.shape
time_axis = torch.arange(0, num_frames) / sample_rate
figure, axes = plt.subplots(num_channels, 1)
if num_channels == 1:
axes = [axes]
for c in range(num_channels):
axes[c].plot(time_axis, waveform[c], linewidth=1)
axes[c].grid(True)
if num_channels > 1:
axes[c].set_ylabel(f"Channel {c+1}")
if xlim:
axes[c].set_xlim(xlim)
if ylim:
axes[c].set_ylim(ylim)
figure.suptitle(title)
plt.show(block=False)
def play_audio(waveform, sample_rate):
waveform = waveform.numpy()
num_channels, num_frames = waveform.shape
if num_channels == 1:
display(Audio(waveform[0], rate=sample_rate))
elif num_channels == 2:
display(Audio((waveform[0], waveform[1]), rate=sample_rate))
else:
raise ValueError("Waveform with more than 2 channels are not supported.")
def plot_mel_fbank(fbank, title=None):
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 1)
axs.set_title(title or "Filter bank")
axs.imshow(fbank, aspect="auto")
axs.set_ylabel("frequency bin")
axs.set_xlabel("mel bin")
plt.show(block=False)
def plot_pitch(waveform, sample_rate, pitch):
figure, axis = plt.subplots(1, 1)
axis.set_title("Pitch Feature")
axis.grid(True)
end_time = waveform.shape[1] / sample_rate
time_axis = torch.linspace(0, end_time, waveform.shape[1])
axis.plot(time_axis, waveform[0], linewidth=1, color="gray", alpha=0.3)
axis2 = axis.twinx()
time_axis = torch.linspace(0, end_time, pitch.shape[1])
axis2.plot(time_axis, pitch[0], linewidth=2, label="Pitch", color="green")
axis2.legend(loc=0)
plt.show(block=False)
def plot_kaldi_pitch(waveform, sample_rate, pitch, nfcc):
figure, axis = plt.subplots(1, 1)
axis.set_title("Kaldi Pitch Feature")
axis.grid(True)
end_time = waveform.shape[1] / sample_rate
time_axis = torch.linspace(0, end_time, waveform.shape[1])
axis.plot(time_axis, waveform[0], linewidth=1, color="gray", alpha=0.3)
time_axis = torch.linspace(0, end_time, pitch.shape[1])
ln1 = axis.plot(time_axis, pitch[0], linewidth=2, label="Pitch", color="green")
axis.set_ylim((-1.3, 1.3))
axis2 = axis.twinx()
time_axis = torch.linspace(0, end_time, nfcc.shape[1])
ln2 = axis2.plot(time_axis, nfcc[0], linewidth=2, label="NFCC", color="blue", linestyle="--")
lns = ln1 + ln2
labels = [l.get_label() for l in lns]
axis.legend(lns, labels, loc=0)
plt.show(block=False)
光谱图¶
要获取音频信号随时间变化的频率组成,
您可以使用 .torchaudio.functional.Spectrogram()
waveform, sample_rate = get_speech_sample()
n_fft = 1024
win_length = None
hop_length = 512
# define transformation
spectrogram = T.Spectrogram(
n_fft=n_fft,
win_length=win_length,
hop_length=hop_length,
center=True,
pad_mode="reflect",
power=2.0,
)
# Perform transformation
spec = spectrogram(waveform)
print_stats(spec)
plot_spectrogram(spec[0], title="torchaudio")
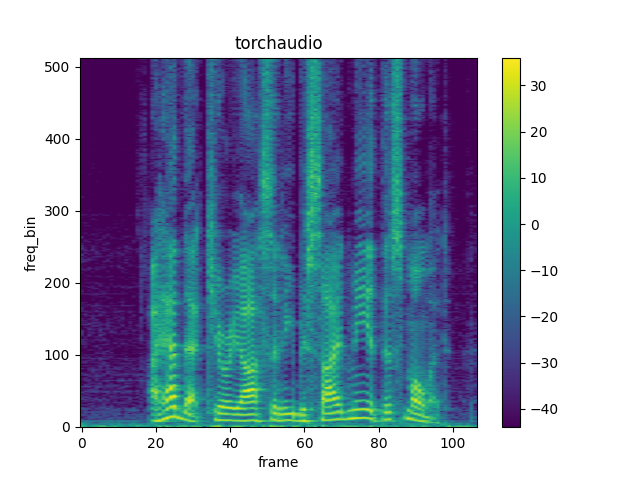
外:
Shape: (1, 513, 107)
Dtype: torch.float32
- Max: 4000.533
- Min: 0.000
- Mean: 5.726
- Std Dev: 70.301
tensor([[[7.8743e+00, 4.4462e+00, 5.6781e-01, ..., 2.7694e+01,
8.9546e+00, 4.1289e+00],
[7.1094e+00, 3.2595e+00, 7.3520e-01, ..., 1.7141e+01,
4.4812e+00, 8.0840e-01],
[3.8374e+00, 8.2490e-01, 3.0779e-01, ..., 1.8502e+00,
1.1777e-01, 1.2369e-01],
...,
[3.4699e-07, 1.0605e-05, 1.2395e-05, ..., 7.4096e-06,
8.2065e-07, 1.0176e-05],
[4.7173e-05, 4.4330e-07, 3.9445e-05, ..., 3.0623e-05,
3.9746e-07, 8.1572e-06],
[1.3221e-04, 1.6440e-05, 7.2536e-05, ..., 5.4662e-05,
1.1663e-05, 2.5758e-06]]])
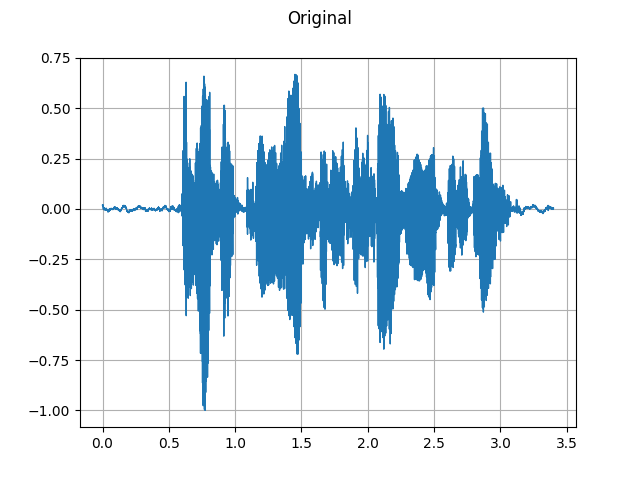
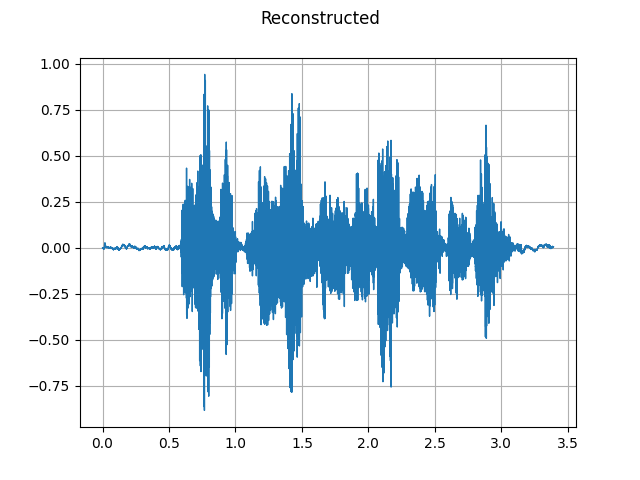
格里芬林¶
要从频谱图中恢复波形,可以使用 。GriffinLim
torch.random.manual_seed(0)
waveform, sample_rate = get_speech_sample()
plot_waveform(waveform, sample_rate, title="Original")
play_audio(waveform, sample_rate)
n_fft = 1024
win_length = None
hop_length = 512
spec = T.Spectrogram(
n_fft=n_fft,
win_length=win_length,
hop_length=hop_length,
)(waveform)
griffin_lim = T.GriffinLim(
n_fft=n_fft,
win_length=win_length,
hop_length=hop_length,
)
waveform = griffin_lim(spec)
plot_waveform(waveform, sample_rate, title="Reconstructed")
play_audio(waveform, sample_rate)
外:
<IPython.lib.display.Audio object>
<IPython.lib.display.Audio object>
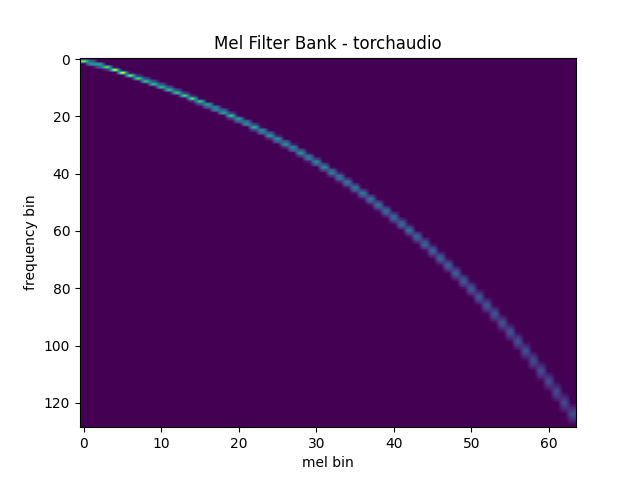
梅尔滤波器组¶
torchaudio.functional.melscale_fbanks()生成滤波器组
用于将频率 bin 转换为 mel-scale bin 。
由于此功能不需要输入音频/功能,因此没有
等效转换torchaudio.transforms().
n_fft = 256
n_mels = 64
sample_rate = 6000
mel_filters = F.melscale_fbanks(
int(n_fft // 2 + 1),
n_mels=n_mels,
f_min=0.0,
f_max=sample_rate / 2.0,
sample_rate=sample_rate,
norm="slaney",
)
plot_mel_fbank(mel_filters, "Mel Filter Bank - torchaudio")
与 librosa 的比较¶
作为参考,这是获取 mel 滤波器组的等效方法
跟。librosa
mel_filters_librosa = librosa.filters.mel(
sr=sample_rate,
n_fft=n_fft,
n_mels=n_mels,
fmin=0.0,
fmax=sample_rate / 2.0,
norm="slaney",
htk=True,
).T
plot_mel_fbank(mel_filters_librosa, "Mel Filter Bank - librosa")
mse = torch.square(mel_filters - mel_filters_librosa).mean().item()
print("Mean Square Difference: ", mse)
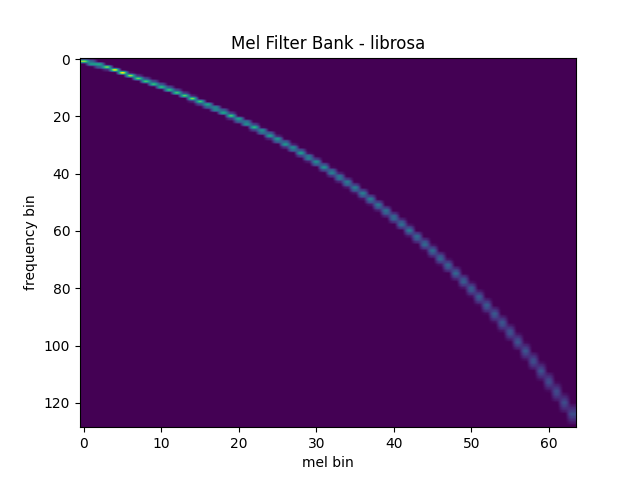
外:
Mean Square Difference: 3.795462323290159e-17
MelSpectrogram 梅尔频谱图¶
生成梅尔尺度频谱图涉及生成频谱图
以及执行 mel-scale 转换。在torchaudiotorchaudio.transforms.MelSpectrogram()提供
此功能。
waveform, sample_rate = get_speech_sample()
n_fft = 1024
win_length = None
hop_length = 512
n_mels = 128
mel_spectrogram = T.MelSpectrogram(
sample_rate=sample_rate,
n_fft=n_fft,
win_length=win_length,
hop_length=hop_length,
center=True,
pad_mode="reflect",
power=2.0,
norm="slaney",
onesided=True,
n_mels=n_mels,
mel_scale="htk",
)
melspec = mel_spectrogram(waveform)
plot_spectrogram(melspec[0], title="MelSpectrogram - torchaudio", ylabel="mel freq")
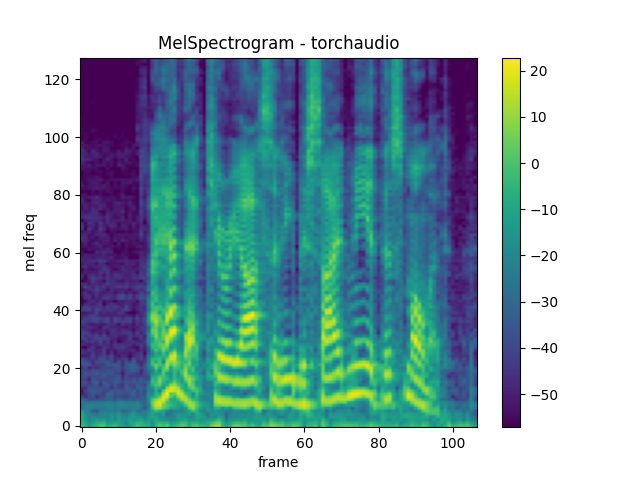
与 librosa 的比较¶
作为参考,以下是生成 mel-scale 的等效方法
具有 的频谱图 。librosa
melspec_librosa = librosa.feature.melspectrogram(
y=waveform.numpy()[0],
sr=sample_rate,
n_fft=n_fft,
hop_length=hop_length,
win_length=win_length,
center=True,
pad_mode="reflect",
power=2.0,
n_mels=n_mels,
norm="slaney",
htk=True,
)
plot_spectrogram(melspec_librosa, title="MelSpectrogram - librosa", ylabel="mel freq")
mse = torch.square(melspec - melspec_librosa).mean().item()
print("Mean Square Difference: ", mse)
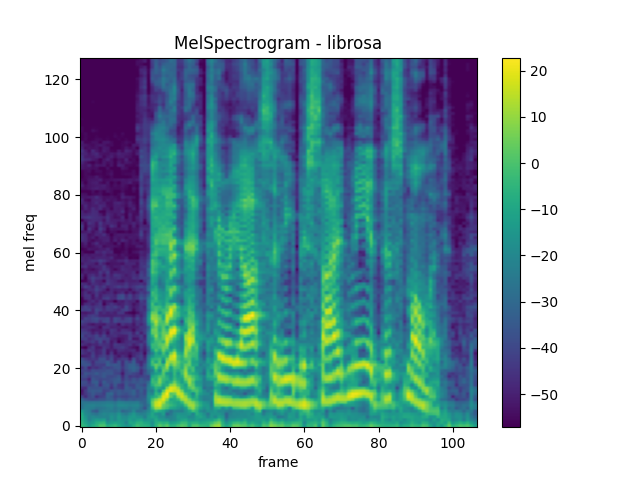
外:
Mean Square Difference: 1.1827383517015733e-10
MFCC¶
waveform, sample_rate = get_speech_sample()
n_fft = 2048
win_length = None
hop_length = 512
n_mels = 256
n_mfcc = 256
mfcc_transform = T.MFCC(
sample_rate=sample_rate,
n_mfcc=n_mfcc,
melkwargs={
"n_fft": n_fft,
"n_mels": n_mels,
"hop_length": hop_length,
"mel_scale": "htk",
},
)
mfcc = mfcc_transform(waveform)
plot_spectrogram(mfcc[0])
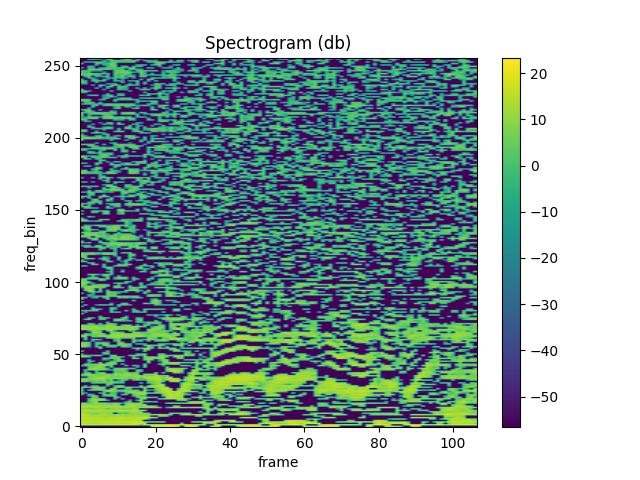
与 librosa 的比较¶
melspec = librosa.feature.melspectrogram(
y=waveform.numpy()[0],
sr=sample_rate,
n_fft=n_fft,
win_length=win_length,
hop_length=hop_length,
n_mels=n_mels,
htk=True,
norm=None,
)
mfcc_librosa = librosa.feature.mfcc(
S=librosa.core.spectrum.power_to_db(melspec),
n_mfcc=n_mfcc,
dct_type=2,
norm="ortho",
)
plot_spectrogram(mfcc_librosa)
mse = torch.square(mfcc - mfcc_librosa).mean().item()
print("Mean Square Difference: ", mse)
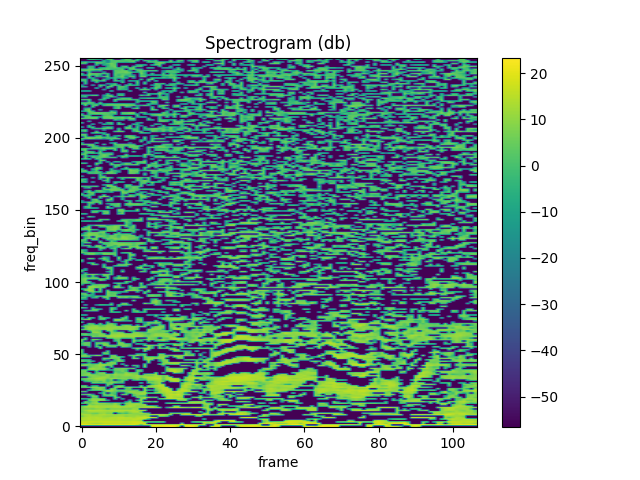
外:
Mean Square Difference: 1.0665760040283203
投¶
waveform, sample_rate = get_speech_sample()
pitch = F.detect_pitch_frequency(waveform, sample_rate)
plot_pitch(waveform, sample_rate, pitch)
play_audio(waveform, sample_rate)
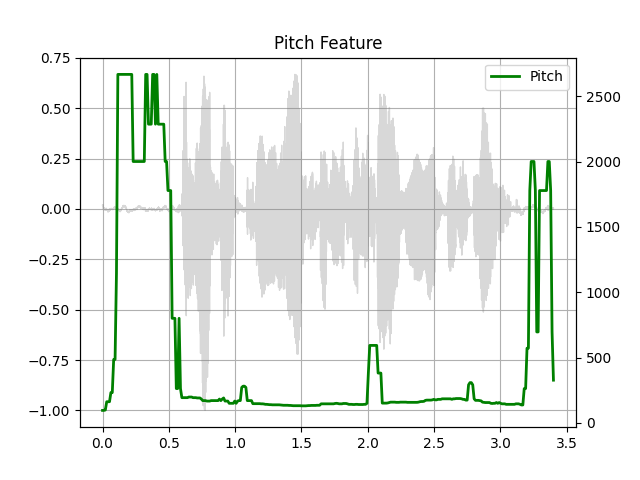
外:
<IPython.lib.display.Audio object>
Kaldi Pitch(测试版)¶
Kaldi Pitch 功能 [1] 是一种针对自动调整的 Pitch 检测机制
语音识别 (ASR) 应用程序。这是 中的一个 beta 功能。
它以torchaudiotorchaudio.functional.compute_kaldi_pitch().
针对自动语音识别进行调整的音高提取算法
Ghahremani、B. BabaAli、D. Povey、K. Riedhammer、J. Trmal 和 S. 库丹普尔
2014 IEEE声学、语音与信号国际会议 加工 (ICASSP),佛罗伦萨,2014 年,第 2494-2498 页,doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2014.6854049。 [摘要], [论文]
waveform, sample_rate = get_speech_sample(resample=16000)
pitch_feature = F.compute_kaldi_pitch(waveform, sample_rate)
pitch, nfcc = pitch_feature[..., 0], pitch_feature[..., 1]
plot_kaldi_pitch(waveform, sample_rate, pitch, nfcc)
play_audio(waveform, sample_rate)
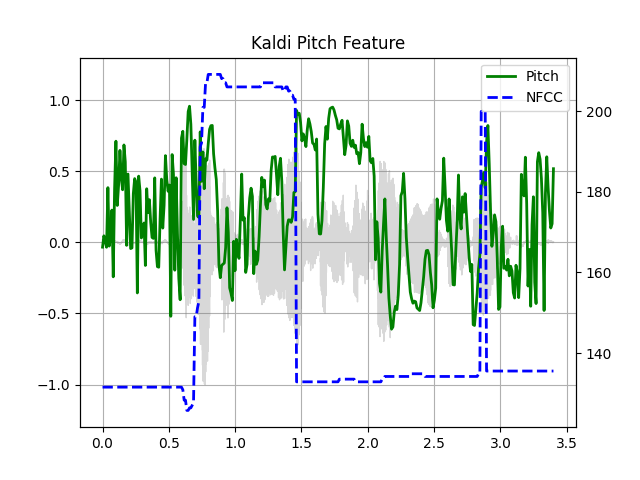
外:
<IPython.lib.display.Audio object>
脚本总运行时间:(0 分 4.249 秒)