注意
单击此处下载完整的示例代码
音频数据增强¶
torchaudio提供了多种方法来增强音频数据。
import torch
import torchaudio
import torchaudio.functional as F
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
外:
1.11.0+cpu
0.11.0+cpu
准备数据和实用程序函数(跳过本节)¶
# @title Prepare data and utility functions. {display-mode: "form"}
# @markdown
# @markdown You do not need to look into this cell.
# @markdown Just execute once and you are good to go.
# @markdown
# @markdown In this tutorial, we will use a speech data from [VOiCES dataset](https://iqtlabs.github.io/voices/),
# @markdown which is licensed under Creative Commos BY 4.0.
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Preparation of data and helper functions.
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import math
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import requests
from IPython.display import Audio, display
_SAMPLE_DIR = "_assets"
SAMPLE_WAV_URL = "https://pytorch-tutorial-assets.s3.amazonaws.com/steam-train-whistle-daniel_simon.wav"
SAMPLE_WAV_PATH = os.path.join(_SAMPLE_DIR, "steam.wav")
SAMPLE_RIR_URL = "https://pytorch-tutorial-assets.s3.amazonaws.com/VOiCES_devkit/distant-16k/room-response/rm1/impulse/Lab41-SRI-VOiCES-rm1-impulse-mc01-stu-clo.wav" # noqa: E501
SAMPLE_RIR_PATH = os.path.join(_SAMPLE_DIR, "rir.wav")
SAMPLE_WAV_SPEECH_URL = "https://pytorch-tutorial-assets.s3.amazonaws.com/VOiCES_devkit/source-16k/train/sp0307/Lab41-SRI-VOiCES-src-sp0307-ch127535-sg0042.wav" # noqa: E501
SAMPLE_WAV_SPEECH_PATH = os.path.join(_SAMPLE_DIR, "speech.wav")
SAMPLE_NOISE_URL = "https://pytorch-tutorial-assets.s3.amazonaws.com/VOiCES_devkit/distant-16k/distractors/rm1/babb/Lab41-SRI-VOiCES-rm1-babb-mc01-stu-clo.wav" # noqa: E501
SAMPLE_NOISE_PATH = os.path.join(_SAMPLE_DIR, "bg.wav")
os.makedirs(_SAMPLE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
def _fetch_data():
uri = [
(SAMPLE_WAV_URL, SAMPLE_WAV_PATH),
(SAMPLE_RIR_URL, SAMPLE_RIR_PATH),
(SAMPLE_WAV_SPEECH_URL, SAMPLE_WAV_SPEECH_PATH),
(SAMPLE_NOISE_URL, SAMPLE_NOISE_PATH),
]
for url, path in uri:
with open(path, "wb") as file_:
file_.write(requests.get(url).content)
_fetch_data()
def _get_sample(path, resample=None):
effects = [["remix", "1"]]
if resample:
effects.extend(
[
["lowpass", f"{resample // 2}"],
["rate", f"{resample}"],
]
)
return torchaudio.sox_effects.apply_effects_file(path, effects=effects)
def get_sample(*, resample=None):
return _get_sample(SAMPLE_WAV_PATH, resample=resample)
def get_speech_sample(*, resample=None):
return _get_sample(SAMPLE_WAV_SPEECH_PATH, resample=resample)
def plot_waveform(waveform, sample_rate, title="Waveform", xlim=None, ylim=None):
waveform = waveform.numpy()
num_channels, num_frames = waveform.shape
time_axis = torch.arange(0, num_frames) / sample_rate
figure, axes = plt.subplots(num_channels, 1)
if num_channels == 1:
axes = [axes]
for c in range(num_channels):
axes[c].plot(time_axis, waveform[c], linewidth=1)
axes[c].grid(True)
if num_channels > 1:
axes[c].set_ylabel(f"Channel {c+1}")
if xlim:
axes[c].set_xlim(xlim)
if ylim:
axes[c].set_ylim(ylim)
figure.suptitle(title)
plt.show(block=False)
def print_stats(waveform, sample_rate=None, src=None):
if src:
print("-" * 10)
print("Source:", src)
print("-" * 10)
if sample_rate:
print("Sample Rate:", sample_rate)
print("Shape:", tuple(waveform.shape))
print("Dtype:", waveform.dtype)
print(f" - Max: {waveform.max().item():6.3f}")
print(f" - Min: {waveform.min().item():6.3f}")
print(f" - Mean: {waveform.mean().item():6.3f}")
print(f" - Std Dev: {waveform.std().item():6.3f}")
print()
print(waveform)
print()
def plot_specgram(waveform, sample_rate, title="Spectrogram", xlim=None):
waveform = waveform.numpy()
num_channels, num_frames = waveform.shape
figure, axes = plt.subplots(num_channels, 1)
if num_channels == 1:
axes = [axes]
for c in range(num_channels):
axes[c].specgram(waveform[c], Fs=sample_rate)
if num_channels > 1:
axes[c].set_ylabel(f"Channel {c+1}")
if xlim:
axes[c].set_xlim(xlim)
figure.suptitle(title)
plt.show(block=False)
def play_audio(waveform, sample_rate):
waveform = waveform.numpy()
num_channels, num_frames = waveform.shape
if num_channels == 1:
return Audio(waveform[0], rate=sample_rate)
elif num_channels == 2:
return Audio((waveform[0], waveform[1]), rate=sample_rate)
else:
raise ValueError("Waveform with more than 2 channels are not supported.")
def get_rir_sample(*, resample=None, processed=False):
rir_raw, sample_rate = _get_sample(SAMPLE_RIR_PATH, resample=resample)
if not processed:
return rir_raw, sample_rate
rir = rir_raw[:, int(sample_rate * 1.01) : int(sample_rate * 1.3)]
rir = rir / torch.norm(rir, p=2)
rir = torch.flip(rir, [1])
return rir, sample_rate
def get_noise_sample(*, resample=None):
return _get_sample(SAMPLE_NOISE_PATH, resample=resample)
应用效果和筛选¶
torchaudio.sox_effects()允许直接应用类似于
可用于 Tensor 对象和 file 对象音频源。sox
有两个函数可用于此:
torchaudio.sox_effects.apply_effects_tensor()用于应用效果 到 Tensor 中。torchaudio.sox_effects.apply_effects_file()用于将效果应用于 其他音频源。
这两个函数都接受 .
这与 command 的工作方式基本一致,但需要注意的是
,它会自动添加一些效果,而 的
implementation 则不会。List[List[str]]soxsoxtorchaudio
可用效果列表请参考 SOX 文档。
提示如果您需要动态加载和重新采样音频数据,
然后,您可以使用torchaudio.sox_effects.apply_effects_file()带效果 ."rate"
注意 torchaudio.sox_effects.apply_effects_file()接受
类文件对象或类路径对象。
似torchaudio.load(),当音频格式不能
从文件扩展名或标头推断,您可以提供
参数指定音频源的格式。format
注意这个过程是不可微分的。
# Load the data
waveform1, sample_rate1 = get_sample(resample=16000)
# Define effects
effects = [
["lowpass", "-1", "300"], # apply single-pole lowpass filter
["speed", "0.8"], # reduce the speed
# This only changes sample rate, so it is necessary to
# add `rate` effect with original sample rate after this.
["rate", f"{sample_rate1}"],
["reverb", "-w"], # Reverbration gives some dramatic feeling
]
# Apply effects
waveform2, sample_rate2 = torchaudio.sox_effects.apply_effects_tensor(waveform1, sample_rate1, effects)
print_stats(waveform1, sample_rate=sample_rate1, src="Original")
print_stats(waveform2, sample_rate=sample_rate2, src="Effects Applied")
外:
----------
Source: Original
----------
Sample Rate: 16000
Shape: (1, 39680)
Dtype: torch.float32
- Max: 0.507
- Min: -0.448
- Mean: -0.000
- Std Dev: 0.122
tensor([[ 0.0007, 0.0076, 0.0122, ..., -0.0049, -0.0025, 0.0020]])
----------
Source: Effects Applied
----------
Sample Rate: 16000
Shape: (2, 49600)
Dtype: torch.float32
- Max: 0.091
- Min: -0.091
- Mean: -0.000
- Std Dev: 0.021
tensor([[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, ..., 0.0069, 0.0058, 0.0045],
[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, ..., 0.0085, 0.0085, 0.0085]])
请注意,帧数和通道数与 应用效果后的原始值。让我们听听 音频。
源语言:¶
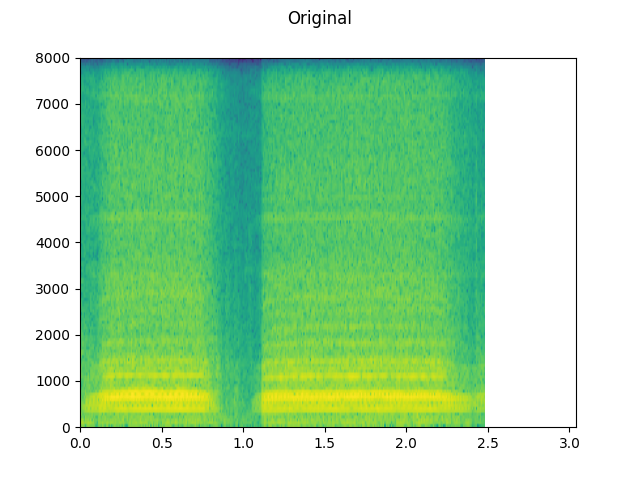
plot_waveform(waveform1, sample_rate1, title="Original", xlim=(-0.1, 3.2))
plot_specgram(waveform1, sample_rate1, title="Original", xlim=(0, 3.04))
play_audio(waveform1, sample_rate1)
应用的效果:¶
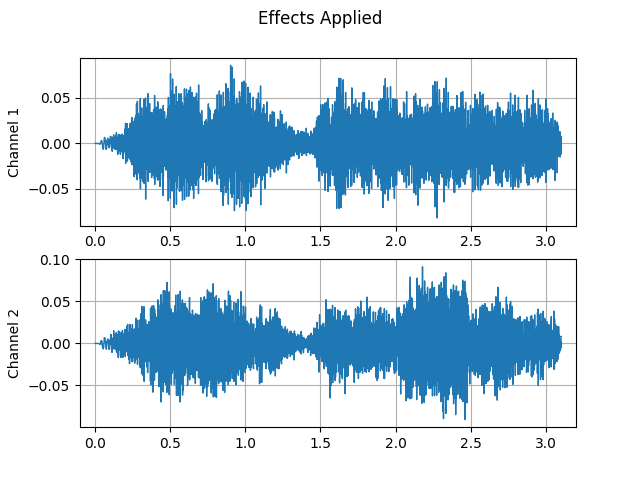
plot_waveform(waveform2, sample_rate2, title="Effects Applied", xlim=(-0.1, 3.2))
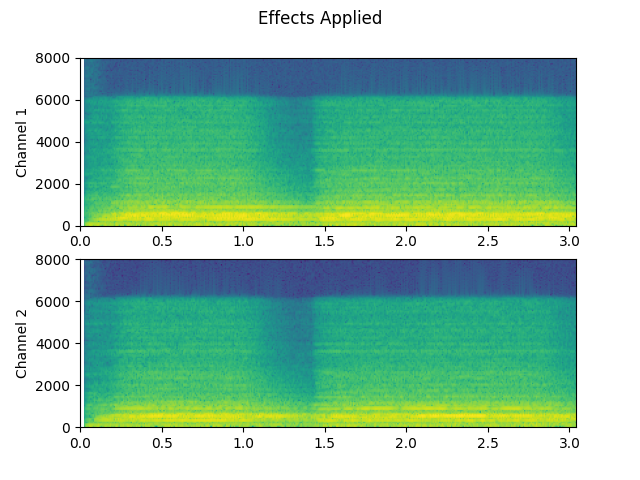
plot_specgram(waveform2, sample_rate2, title="Effects Applied", xlim=(0, 3.04))
play_audio(waveform2, sample_rate2)
听起来是不是更戏剧化?
模拟 Room 混响¶
卷积 reverb 是一个 技术,用于使干净的音频听起来像以前一样 在不同的环境中生产。
例如,使用房间脉冲响应 (RIR),我们可以制作干净的语音 听起来就像是在会议室里说的一样。
对于此过程,我们需要 RIR 数据。以下数据来自 VOiCES 数据集,但您可以录制自己的数据集 — 只需打开麦克风即可 并拍手。
sample_rate = 8000
rir_raw, _ = get_rir_sample(resample=sample_rate)
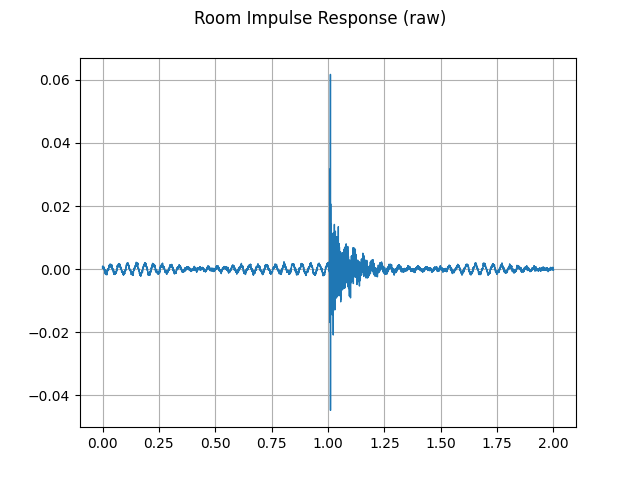
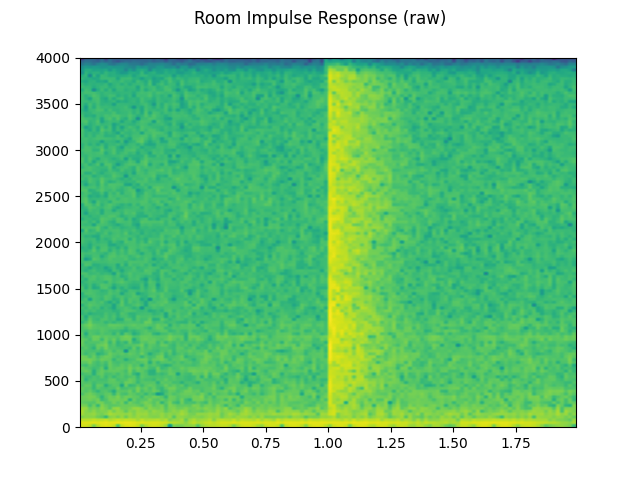
plot_waveform(rir_raw, sample_rate, title="Room Impulse Response (raw)", ylim=None)
plot_specgram(rir_raw, sample_rate, title="Room Impulse Response (raw)")
play_audio(rir_raw, sample_rate)
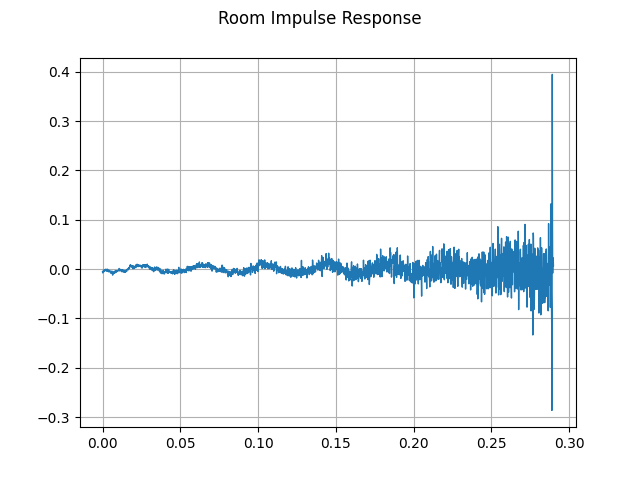
首先,我们需要清理 RIR。我们提取主要脉冲,归一化 信号 power,然后沿时间轴翻转。
rir = rir_raw[:, int(sample_rate * 1.01) : int(sample_rate * 1.3)]
rir = rir / torch.norm(rir, p=2)
rir = torch.flip(rir, [1])
print_stats(rir)
plot_waveform(rir, sample_rate, title="Room Impulse Response", ylim=None)
外:
Shape: (1, 2320)
Dtype: torch.float32
- Max: 0.395
- Min: -0.286
- Mean: -0.000
- Std Dev: 0.021
tensor([[-0.0052, -0.0076, -0.0071, ..., 0.0184, 0.0173, 0.0070]])
然后,我们使用 RIR 滤波器对语音信号进行卷积。
speech, _ = get_speech_sample(resample=sample_rate)
speech_ = torch.nn.functional.pad(speech, (rir.shape[1] - 1, 0))
augmented = torch.nn.functional.conv1d(speech_[None, ...], rir[None, ...])[0]
源语言:¶
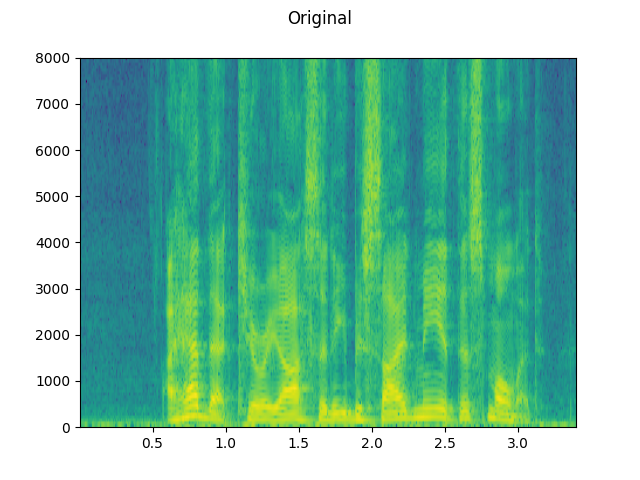
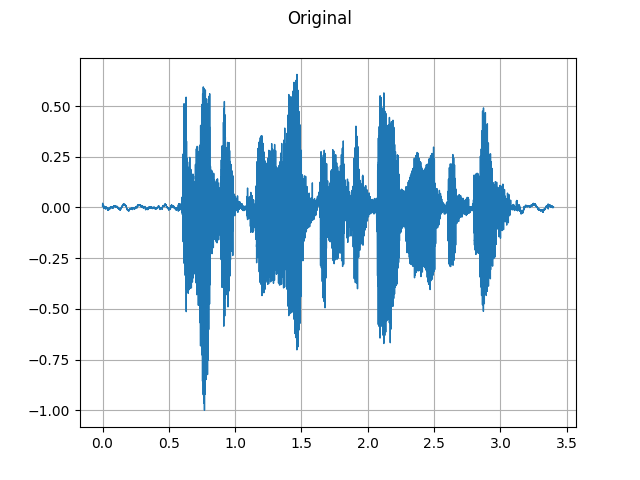
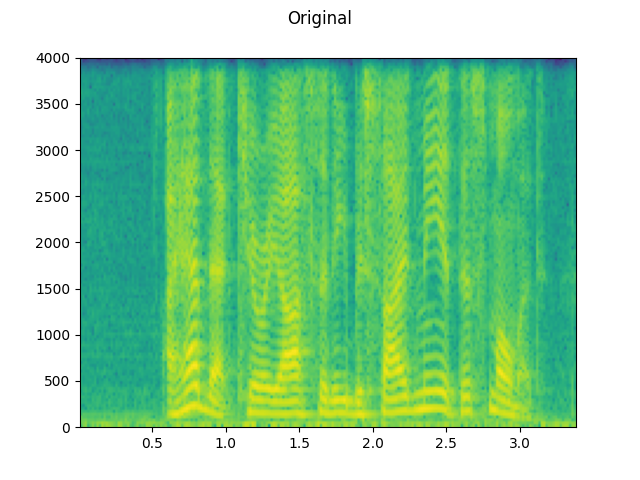
plot_waveform(speech, sample_rate, title="Original", ylim=None)
plot_specgram(speech, sample_rate, title="Original")
play_audio(speech, sample_rate)
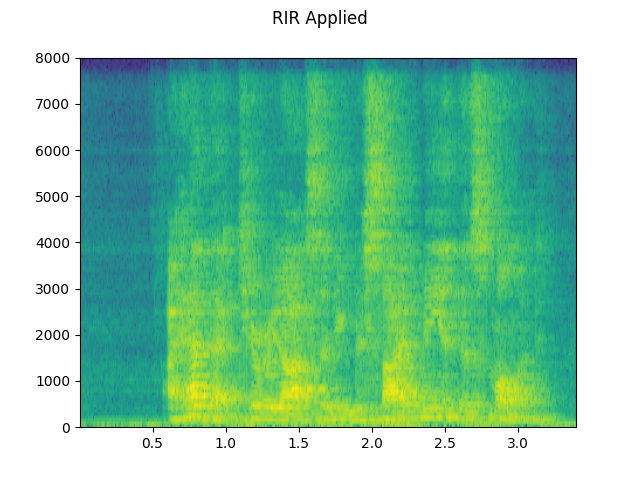
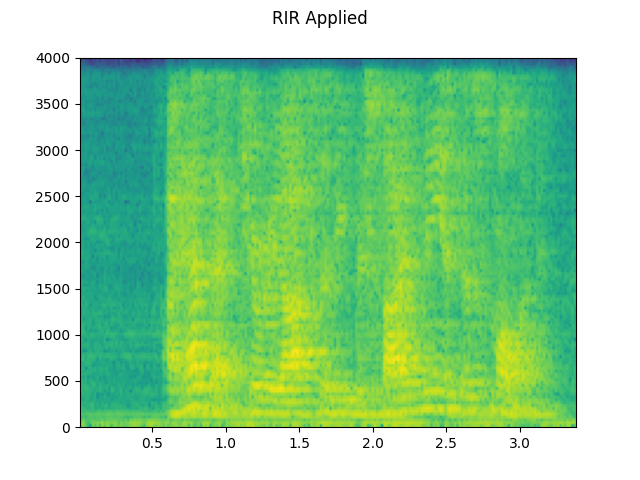
RIR 适用范围:¶
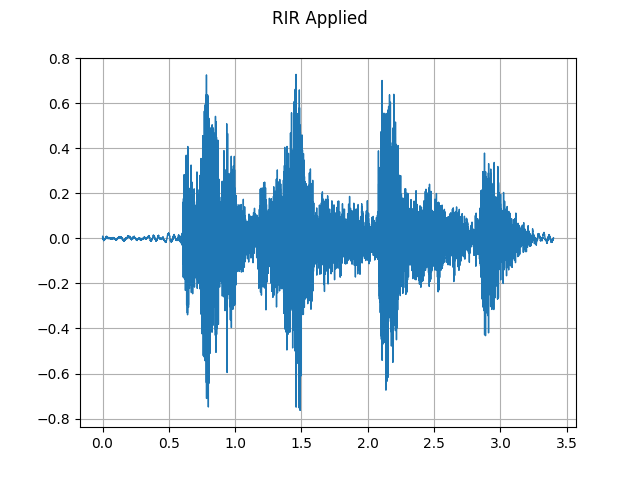
plot_waveform(augmented, sample_rate, title="RIR Applied", ylim=None)
plot_specgram(augmented, sample_rate, title="RIR Applied")
play_audio(augmented, sample_rate)
添加背景噪声¶
要向音频数据添加背景噪声,只需将噪声 Tensor 添加到 表示音频数据的 Tensor。调整 噪声强度正在改变信噪比 (SNR)。 [维基百科]
$$ \mathrm{SNR} = \frac{P_{信号}}{P_{噪音}} $$
$$ \mathrm{SNR_{dB}} = 10 \log _{{10}} \mathrm {SNR} $$
sample_rate = 8000
speech, _ = get_speech_sample(resample=sample_rate)
noise, _ = get_noise_sample(resample=sample_rate)
noise = noise[:, : speech.shape[1]]
speech_power = speech.norm(p=2)
noise_power = noise.norm(p=2)
snr_dbs = [20, 10, 3]
noisy_speeches = []
for snr_db in snr_dbs:
snr = math.exp(snr_db / 10)
scale = snr * noise_power / speech_power
noisy_speeches.append((scale * speech + noise) / 2)
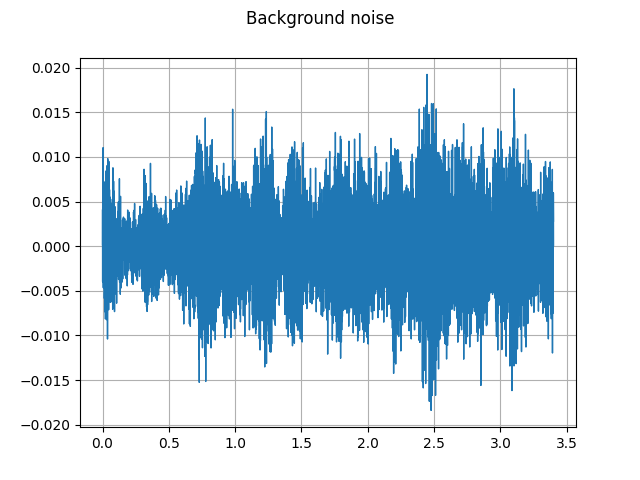
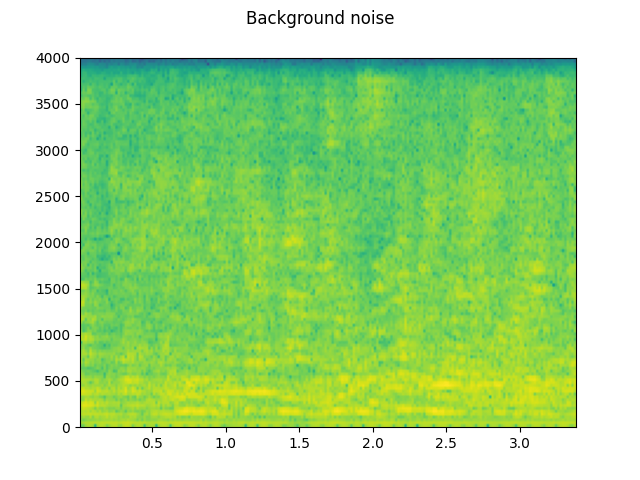
背景噪音:¶
plot_waveform(noise, sample_rate, title="Background noise")
plot_specgram(noise, sample_rate, title="Background noise")
play_audio(noise, sample_rate)
信噪比 20 dB:¶
snr_db, noisy_speech = snr_dbs[0], noisy_speeches[0]
plot_waveform(noisy_speech, sample_rate, title=f"SNR: {snr_db} [dB]")
plot_specgram(noisy_speech, sample_rate, title=f"SNR: {snr_db} [dB]")
play_audio(noisy_speech, sample_rate)
信噪比 10 dB:¶
snr_db, noisy_speech = snr_dbs[1], noisy_speeches[1]
plot_waveform(noisy_speech, sample_rate, title=f"SNR: {snr_db} [dB]")
plot_specgram(noisy_speech, sample_rate, title=f"SNR: {snr_db} [dB]")
play_audio(noisy_speech, sample_rate)
信噪比 3 dB:¶
snr_db, noisy_speech = snr_dbs[2], noisy_speeches[2]
plot_waveform(noisy_speech, sample_rate, title=f"SNR: {snr_db} [dB]")
plot_specgram(noisy_speech, sample_rate, title=f"SNR: {snr_db} [dB]")
play_audio(noisy_speech, sample_rate)
将编解码器应用于 Tensor 对象¶
torchaudio.functional.apply_codec()可以将编解码器应用于
一个 Tensor 对象。
注意这个过程是不可微分的。
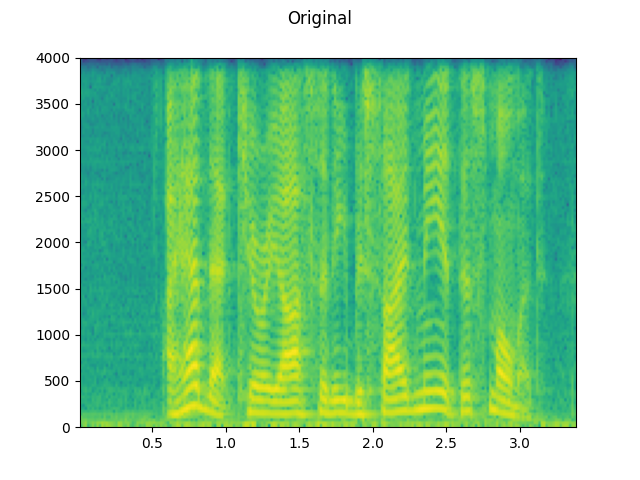
waveform, sample_rate = get_speech_sample(resample=8000)
plot_specgram(waveform, sample_rate, title="Original")
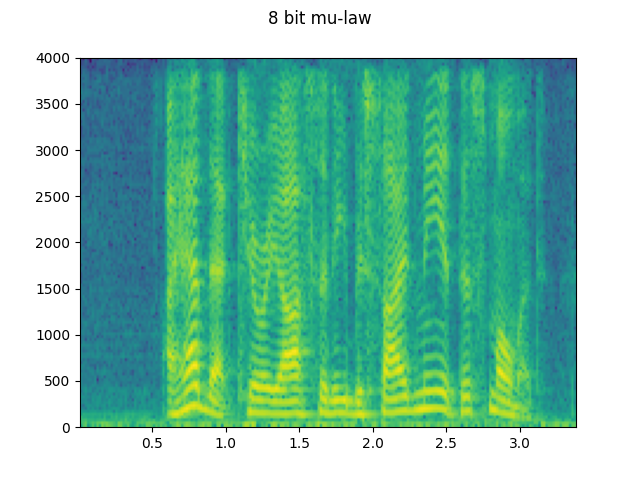
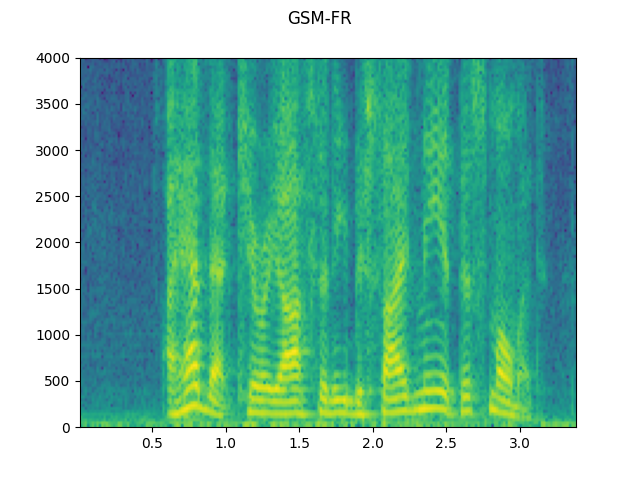
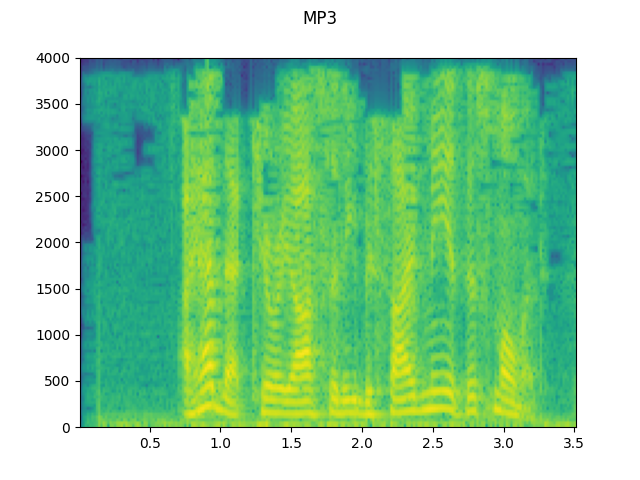
configs = [
({"format": "wav", "encoding": "ULAW", "bits_per_sample": 8}, "8 bit mu-law"),
({"format": "gsm"}, "GSM-FR"),
({"format": "mp3", "compression": -9}, "MP3"),
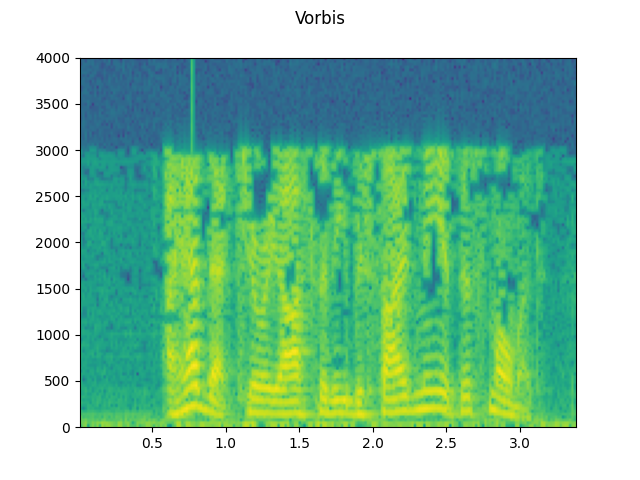
({"format": "vorbis", "compression": -1}, "Vorbis"),
]
waveforms = []
for param, title in configs:
augmented = F.apply_codec(waveform, sample_rate, **param)
plot_specgram(augmented, sample_rate, title=title)
waveforms.append(augmented)
模拟电话重新编码¶
结合前面的技术,我们可以模拟听起来 就像一个人在一个回声房间里通过电话交谈,人们在交谈 在后台。
sample_rate = 16000
original_speech, _ = get_speech_sample(resample=sample_rate)
plot_specgram(original_speech, sample_rate, title="Original")
# Apply RIR
rir, _ = get_rir_sample(resample=sample_rate, processed=True)
speech_ = torch.nn.functional.pad(original_speech, (rir.shape[1] - 1, 0))
rir_applied = torch.nn.functional.conv1d(speech_[None, ...], rir[None, ...])[0]
plot_specgram(rir_applied, sample_rate, title="RIR Applied")
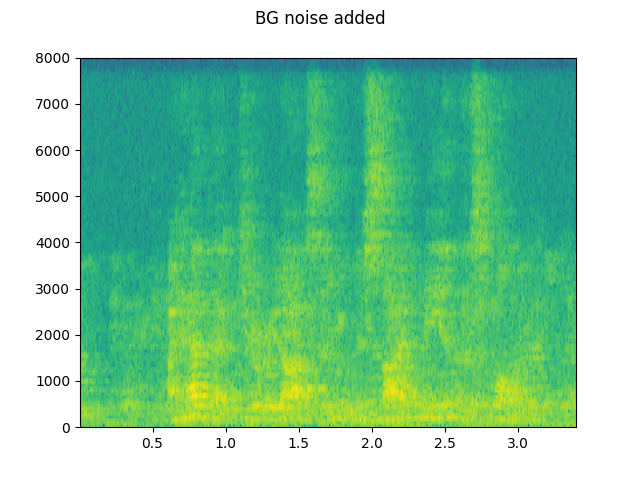
# Add background noise
# Because the noise is recorded in the actual environment, we consider that
# the noise contains the acoustic feature of the environment. Therefore, we add
# the noise after RIR application.
noise, _ = get_noise_sample(resample=sample_rate)
noise = noise[:, : rir_applied.shape[1]]
snr_db = 8
scale = math.exp(snr_db / 10) * noise.norm(p=2) / rir_applied.norm(p=2)
bg_added = (scale * rir_applied + noise) / 2
plot_specgram(bg_added, sample_rate, title="BG noise added")
# Apply filtering and change sample rate
filtered, sample_rate2 = torchaudio.sox_effects.apply_effects_tensor(
bg_added,
sample_rate,
effects=[
["lowpass", "4000"],
[
"compand",
"0.02,0.05",
"-60,-60,-30,-10,-20,-8,-5,-8,-2,-8",
"-8",
"-7",
"0.05",
],
["rate", "8000"],
],
)
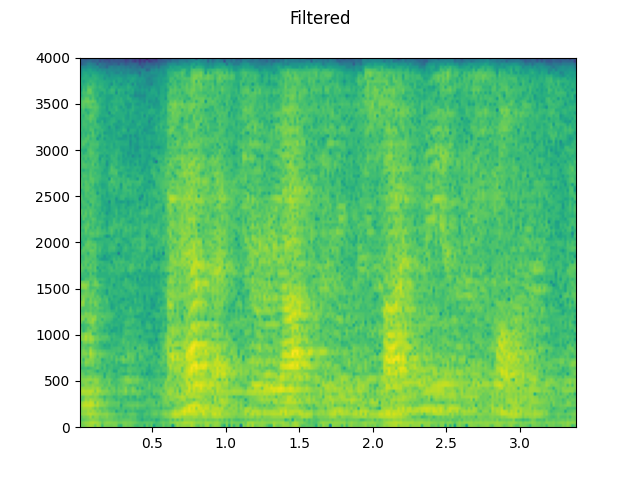
plot_specgram(filtered, sample_rate2, title="Filtered")
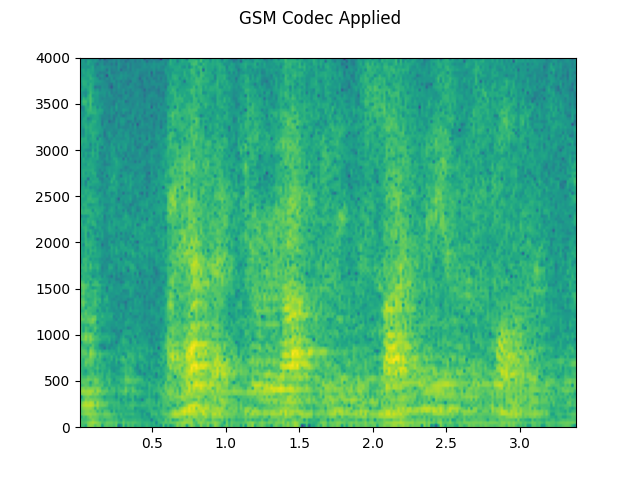
# Apply telephony codec
codec_applied = F.apply_codec(filtered, sample_rate2, format="gsm")
plot_specgram(codec_applied, sample_rate2, title="GSM Codec Applied")
![信噪比: 20 [dB]](https://pytorch.org/audio/0.11.0/_images/sphx_glr_audio_data_augmentation_tutorial_014.png)
![信噪比: 20 [dB]](https://pytorch.org/audio/0.11.0/_images/sphx_glr_audio_data_augmentation_tutorial_015.png)
![信噪比: 10 [dB]](https://pytorch.org/audio/0.11.0/_images/sphx_glr_audio_data_augmentation_tutorial_016.png)
![信噪比: 10 [dB]](https://pytorch.org/audio/0.11.0/_images/sphx_glr_audio_data_augmentation_tutorial_017.png)
![信噪比: 3 [dB]](https://pytorch.org/audio/0.11.0/_images/sphx_glr_audio_data_augmentation_tutorial_018.png)
![信噪比: 3 [dB]](https://pytorch.org/audio/0.11.0/_images/sphx_glr_audio_data_augmentation_tutorial_019.png)