注意
单击此处下载完整的示例代码
使用 Tacotron2 的文本转语音¶
作者: Yao-Yuan Yang, Moto Hira
import IPython
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
概述¶
本教程介绍如何使用 在 torchaudio 中预训练 Tacotron2。
文本转语音管道如下所示:
文本预处理
首先,将输入文本编码为元件列表。在这个 教程中,我们将使用英文字符和音素作为符号。
频谱图生成
从编码的文本中,生成频谱图。为此,我们使用 model。
Tacotron2时域转换
最后一步是将频谱图转换为波形。这 从频谱图生成语音的过程也称为 Vocoder。 在本教程中,使用了三种不同的声码器:
WaveRNN,GriffinLim和 Nvidia 的 WaveGlow 的 WaveGlow 的
整个过程如下图所示。
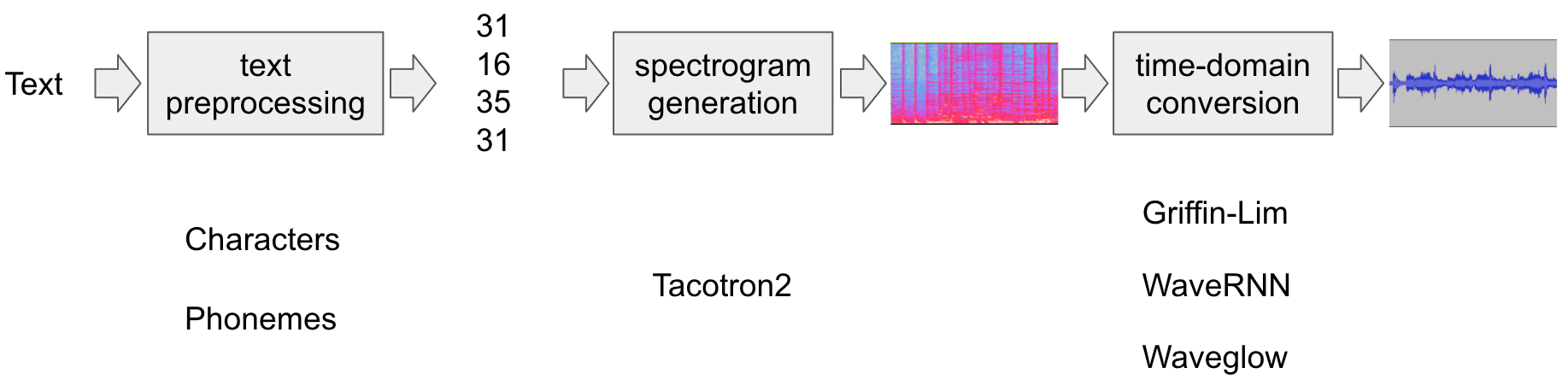
所有相关组件都捆绑在torchaudio.pipelines.Tacotron2TTSBundle,
但本教程还将介绍幕后过程。
制备¶
首先,我们安装必要的依赖项。除了 之外,还需要执行基于音素的
编码。torchaudioDeepPhonemizer
%%bash
pip3 install deep_phonemizer
import torch
import torchaudio
matplotlib.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = [16.0, 4.8]
torch.random.manual_seed(0)
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
print(device)
1.13.1
0.13.1
cpu
文本处理¶
基于字符的编码¶
在本节中,我们将介绍如何使用基于字符的编码 工程。
由于预训练的 Tacotron2 模型需要一组特定的符号
表中,其功能与 中提供的功能相同。这
部分更多地用于解释编码的基础。torchaudio
首先,我们定义品种集。例如,我们可以使用 .然后,我们将映射
输入文本的每个字符都放入相应的
符号。'_-!\'(),.:;? abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
以下是此类处理的示例。在示例中,symbol 不在表中的 API 的 URL 将被忽略。
[19, 16, 23, 23, 26, 11, 34, 26, 29, 23, 15, 2, 11, 31, 16, 35, 31, 11, 31, 26, 11, 30, 27, 16, 16, 14, 19, 2]
如上所述,symbol table 和 indices 必须匹配
预训练的 Tacotron2 模型期望什么。 提供
transform 与预训练模型一起。例如,您可以
instantiate 并使用 type 的 Transform,如下所示。torchaudio
tensor([[19, 16, 23, 23, 26, 11, 34, 26, 29, 23, 15, 2, 11, 31, 16, 35, 31, 11,
31, 26, 11, 30, 27, 16, 16, 14, 19, 2]])
tensor([28], dtype=torch.int32)
该对象将文本或文本列表作为输入。
当提供文本列表时,返回的变量
表示输出中每个已处理令牌的有效长度
批。processorlengths
可以按如下方式检索中间表示。
['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd', '!', ' ', 't', 'e', 'x', 't', ' ', 't', 'o', ' ', 's', 'p', 'e', 'e', 'c', 'h', '!']
基于音素的编码¶
基于音素的编码类似于基于字符的编码,但它 使用基于音素的符号表和 G2P (字素到音素) 型。
G2P 模型的细节不在本教程的讨论范围之内,我们将 看看转换是什么样子的就知道了。
与基于字符的编码类似,编码过程是
预期与预先训练的 Tacotron2 模型的训练对象相匹配。 具有用于创建流程的接口。torchaudio
下面的代码说明了如何创建和使用该过程。后
场景中,使用 package 创建 G2P 模型,并且
作者发布的预训练权重 is
获取。DeepPhonemizerDeepPhonemizer
0%| | 0.00/63.6M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
0%| | 64.0k/63.6M [00:00<03:05, 358kB/s]
0%| | 304k/63.6M [00:00<01:10, 939kB/s]
2%|2 | 1.29M/63.6M [00:00<00:21, 3.11MB/s]
6%|6 | 4.11M/63.6M [00:00<00:07, 8.28MB/s]
11%|#1 | 7.19M/63.6M [00:00<00:05, 11.7MB/s]
16%|#6 | 10.3M/63.6M [00:01<00:04, 13.8MB/s]
21%|## | 13.2M/63.6M [00:01<00:03, 17.2MB/s]
24%|##3 | 15.1M/63.6M [00:01<00:03, 15.2MB/s]
28%|##8 | 18.0M/63.6M [00:01<00:02, 18.5MB/s]
31%|###1 | 20.0M/63.6M [00:01<00:02, 16.3MB/s]
36%|###5 | 22.8M/63.6M [00:01<00:02, 19.3MB/s]
39%|###9 | 25.0M/63.6M [00:01<00:02, 17.1MB/s]
43%|####3 | 27.5M/63.6M [00:02<00:01, 19.3MB/s]
47%|####7 | 30.1M/63.6M [00:02<00:01, 17.9MB/s]
52%|#####1 | 33.1M/63.6M [00:02<00:01, 20.9MB/s]
56%|#####5 | 35.3M/63.6M [00:02<00:01, 18.3MB/s]
60%|###### | 38.2M/63.6M [00:02<00:01, 21.0MB/s]
64%|######3 | 40.7M/63.6M [00:02<00:01, 18.8MB/s]
68%|######8 | 43.3M/63.6M [00:02<00:01, 20.8MB/s]
73%|#######2 | 46.3M/63.6M [00:03<00:00, 19.8MB/s]
77%|#######6 | 48.9M/63.6M [00:03<00:00, 21.5MB/s]
82%|########1 | 52.0M/63.6M [00:03<00:00, 20.5MB/s]
86%|########6 | 54.8M/63.6M [00:03<00:00, 22.4MB/s]
91%|######### | 57.9M/63.6M [00:03<00:00, 21.1MB/s]
95%|#########5| 60.7M/63.6M [00:03<00:00, 22.9MB/s]
100%|##########| 63.6M/63.6M [00:03<00:00, 24.9MB/s]
100%|##########| 63.6M/63.6M [00:03<00:00, 17.7MB/s]
tensor([[54, 20, 65, 69, 11, 92, 44, 65, 38, 2, 11, 81, 40, 64, 79, 81, 11, 81,
20, 11, 79, 77, 59, 37, 2]])
tensor([25], dtype=torch.int32)
请注意,编码值与 基于字符的编码。
中间表示形式如下所示。
['HH', 'AH', 'L', 'OW', ' ', 'W', 'ER', 'L', 'D', '!', ' ', 'T', 'EH', 'K', 'S', 'T', ' ', 'T', 'AH', ' ', 'S', 'P', 'IY', 'CH', '!']
频谱图生成¶
Tacotron2是我们用来从
编码文本。型号详情请参考
纸。
使用预训练权重实例化 Tacotron2 模型很容易, 但是,请注意,需要处理 Tacotron2 模型的输入 通过匹配的文本处理器。
torchaudio.pipelines.Tacotron2TTSBundle捆绑匹配的
模型和处理器组合在一起,以便轻松创建管道。
有关可用的捆绑包及其用法,请参阅Tacotron2TTSBundle.
bundle = torchaudio.pipelines.TACOTRON2_WAVERNN_PHONE_LJSPEECH
processor = bundle.get_text_processor()
tacotron2 = bundle.get_tacotron2().to(device)
text = "Hello world! Text to speech!"
with torch.inference_mode():
processed, lengths = processor(text)
processed = processed.to(device)
lengths = lengths.to(device)
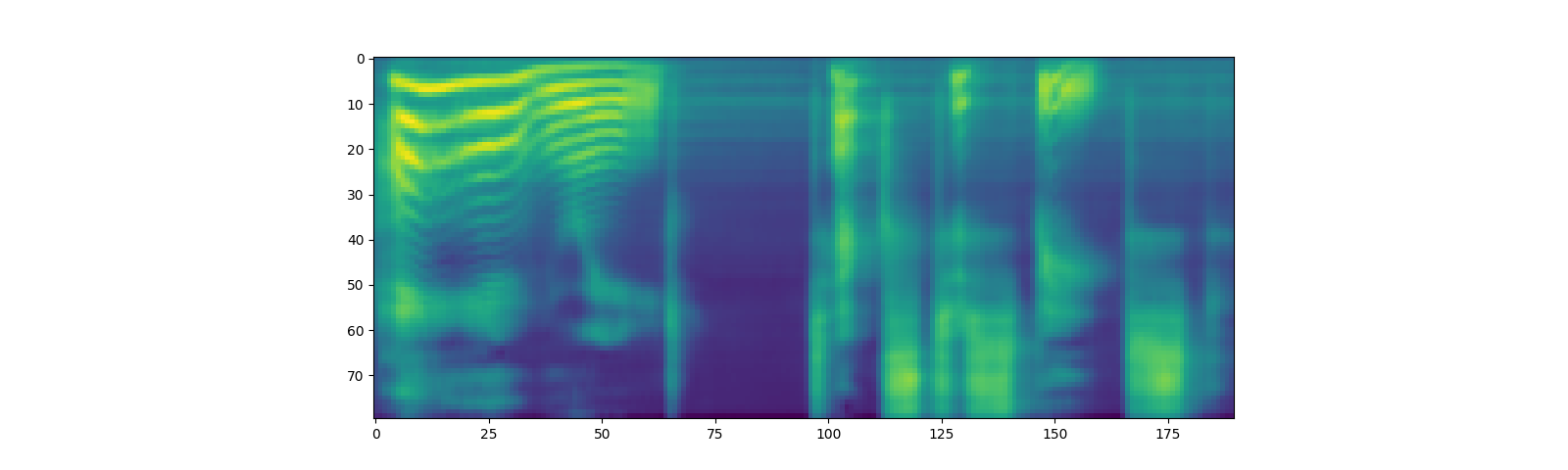
spec, _, _ = tacotron2.infer(processed, lengths)
_ = plt.imshow(spec[0].cpu().detach())
Downloading: "https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/models/tacotron2_english_phonemes_1500_epochs_wavernn_ljspeech.pth" to /root/.cache/torch/hub/checkpoints/tacotron2_english_phonemes_1500_epochs_wavernn_ljspeech.pth
0%| | 0.00/107M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
21%|##1 | 22.7M/107M [00:00<00:00, 238MB/s]
42%|####2 | 45.5M/107M [00:00<00:00, 195MB/s]
65%|######5 | 70.3M/107M [00:00<00:00, 222MB/s]
93%|#########3| 100M/107M [00:00<00:00, 255MB/s]
100%|##########| 107M/107M [00:00<00:00, 244MB/s]
请注意,method perfos multinomial sampling,
因此,生成频谱图的过程会产生随机性。Tacotron2.infer
torch.Size([80, 155])
torch.Size([80, 167])
torch.Size([80, 164])
波形生成¶
生成频谱图后,最后一个过程是恢复 waveform 来自频谱图。
torchaudio提供基于 和 的声码器。GriffinLimWaveRNN
WaveRNN¶
继续上一节,我们可以实例化匹配的 WaveRNN 模型。
bundle = torchaudio.pipelines.TACOTRON2_WAVERNN_PHONE_LJSPEECH
processor = bundle.get_text_processor()
tacotron2 = bundle.get_tacotron2().to(device)
vocoder = bundle.get_vocoder().to(device)
text = "Hello world! Text to speech!"
with torch.inference_mode():
processed, lengths = processor(text)
processed = processed.to(device)
lengths = lengths.to(device)
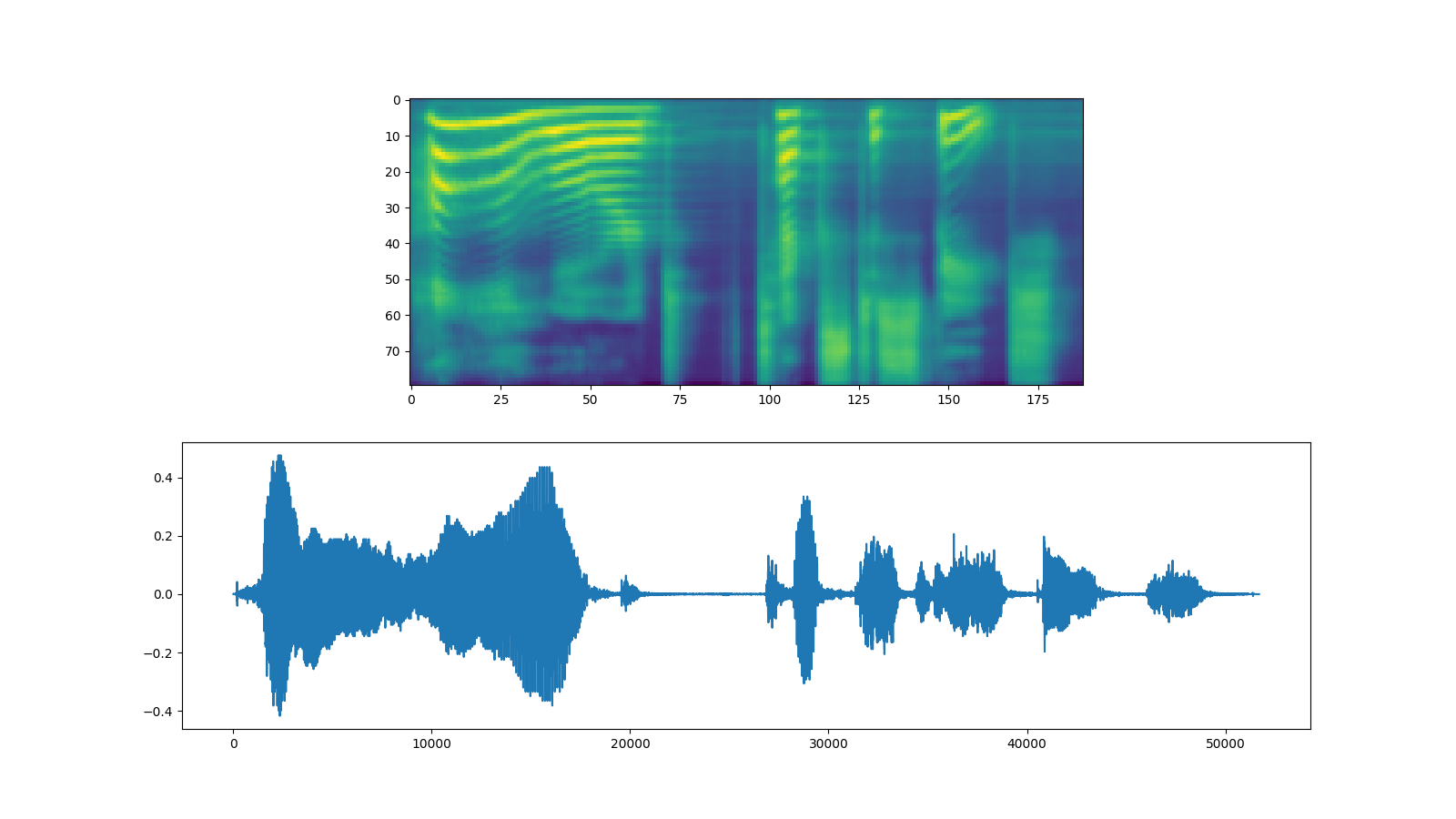
spec, spec_lengths, _ = tacotron2.infer(processed, lengths)
waveforms, lengths = vocoder(spec, spec_lengths)
fig, [ax1, ax2] = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(16, 9))
ax1.imshow(spec[0].cpu().detach())
ax2.plot(waveforms[0].cpu().detach())
IPython.display.Audio(waveforms[0:1].cpu(), rate=vocoder.sample_rate)
Downloading: "https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/models/wavernn_10k_epochs_8bits_ljspeech.pth" to /root/.cache/torch/hub/checkpoints/wavernn_10k_epochs_8bits_ljspeech.pth
0%| | 0.00/16.7M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
100%|##########| 16.7M/16.7M [00:00<00:00, 290MB/s]
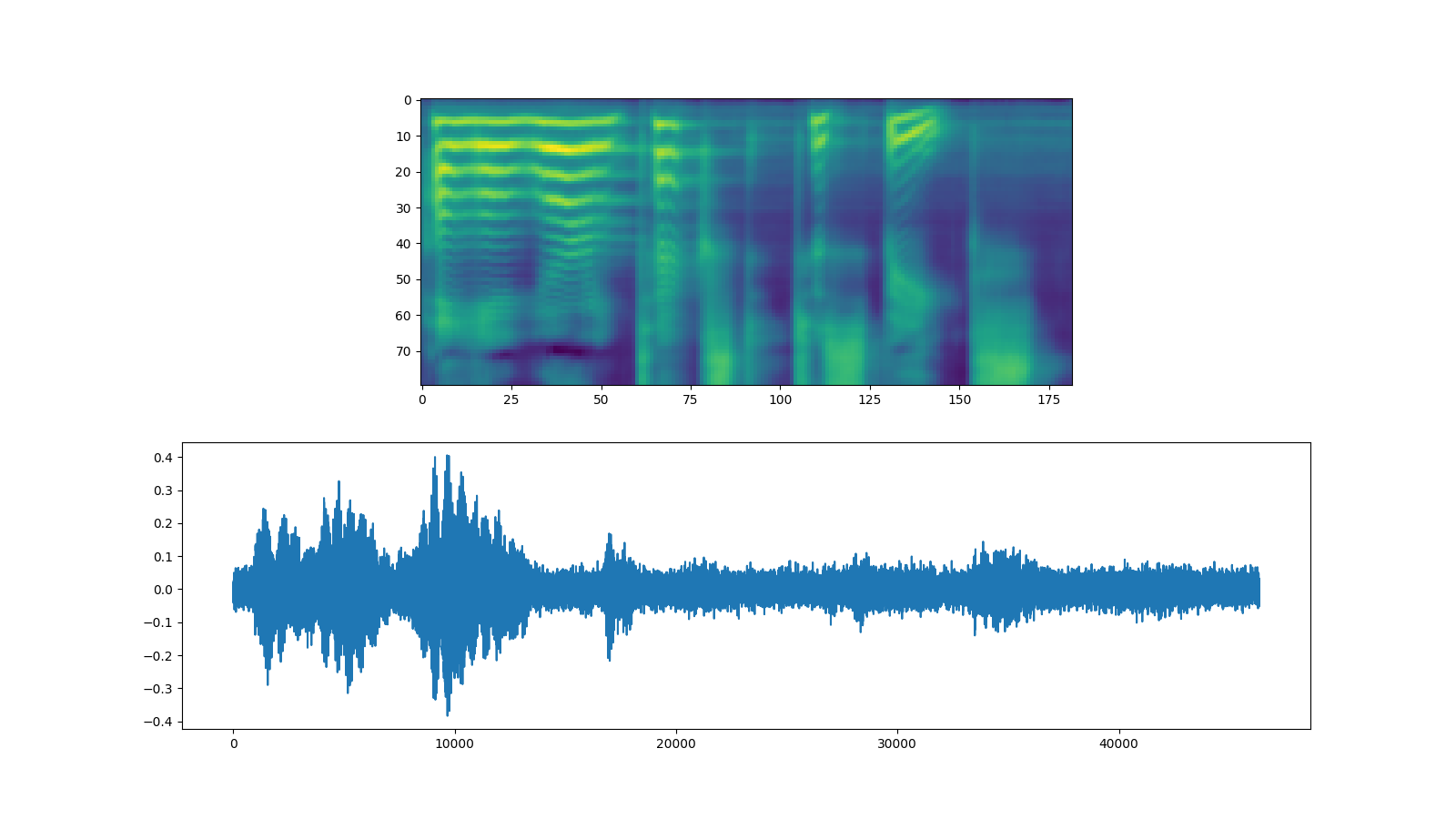
林磊¶
使用 Griffin-Lim 声码器与 WaveRNN 相同。您可以实例化
带有get_vocoder()方法并传递频谱图。
bundle = torchaudio.pipelines.TACOTRON2_GRIFFINLIM_PHONE_LJSPEECH
processor = bundle.get_text_processor()
tacotron2 = bundle.get_tacotron2().to(device)
vocoder = bundle.get_vocoder().to(device)
with torch.inference_mode():
processed, lengths = processor(text)
processed = processed.to(device)
lengths = lengths.to(device)
spec, spec_lengths, _ = tacotron2.infer(processed, lengths)
waveforms, lengths = vocoder(spec, spec_lengths)
fig, [ax1, ax2] = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(16, 9))
ax1.imshow(spec[0].cpu().detach())
ax2.plot(waveforms[0].cpu().detach())
IPython.display.Audio(waveforms[0:1].cpu(), rate=vocoder.sample_rate)
Downloading: "https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/models/tacotron2_english_phonemes_1500_epochs_ljspeech.pth" to /root/.cache/torch/hub/checkpoints/tacotron2_english_phonemes_1500_epochs_ljspeech.pth
0%| | 0.00/107M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
28%|##8 | 30.3M/107M [00:00<00:00, 317MB/s]
56%|#####6 | 60.6M/107M [00:00<00:00, 277MB/s]
88%|########8 | 95.0M/107M [00:00<00:00, 313MB/s]
100%|##########| 107M/107M [00:00<00:00, 305MB/s]
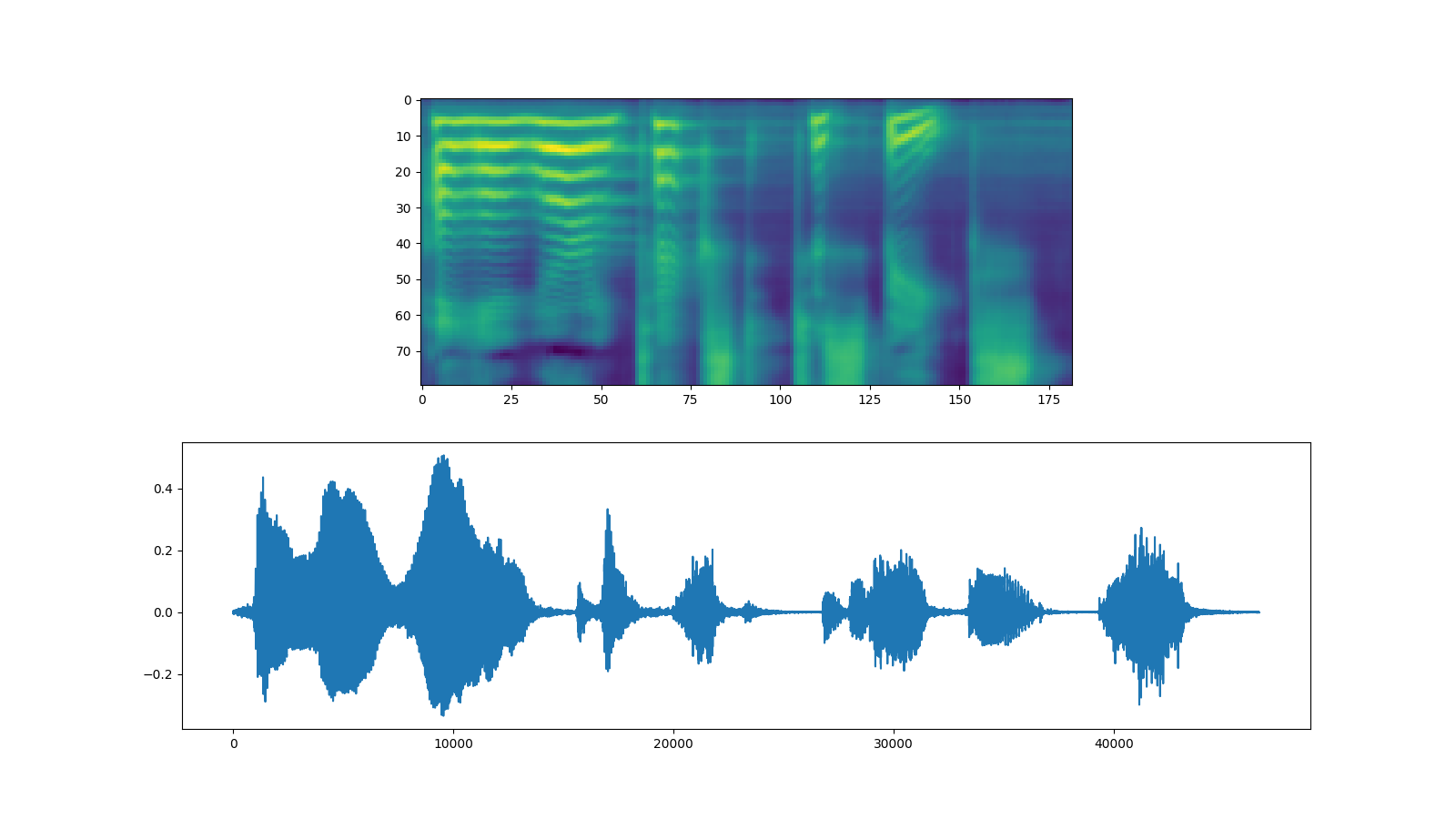
波辉¶
Waveglow 是 Nvidia 发布的声码器。预训练的权重为
发布在 Torch Hub 上。可以使用 module 实例化模型。torch.hub
# Workaround to load model mapped on GPU
# https://stackoverflow.com/a/61840832
waveglow = torch.hub.load(
"NVIDIA/DeepLearningExamples:torchhub",
"nvidia_waveglow",
model_math="fp32",
pretrained=False,
)
checkpoint = torch.hub.load_state_dict_from_url(
"https://api.ngc.nvidia.com/v2/models/nvidia/waveglowpyt_fp32/versions/1/files/nvidia_waveglowpyt_fp32_20190306.pth", # noqa: E501
progress=False,
map_location=device,
)
state_dict = {key.replace("module.", ""): value for key, value in checkpoint["state_dict"].items()}
waveglow.load_state_dict(state_dict)
waveglow = waveglow.remove_weightnorm(waveglow)
waveglow = waveglow.to(device)
waveglow.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
waveforms = waveglow.infer(spec)
fig, [ax1, ax2] = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(16, 9))
ax1.imshow(spec[0].cpu().detach())
ax2.plot(waveforms[0].cpu().detach())
IPython.display.Audio(waveforms[0:1].cpu(), rate=22050)
/usr/local/envs/python3.8/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/hub.py:267: UserWarning: You are about to download and run code from an untrusted repository. In a future release, this won't be allowed. To add the repository to your trusted list, change the command to {calling_fn}(..., trust_repo=False) and a command prompt will appear asking for an explicit confirmation of trust, or load(..., trust_repo=True), which will assume that the prompt is to be answered with 'yes'. You can also use load(..., trust_repo='check') which will only prompt for confirmation if the repo is not already trusted. This will eventually be the default behaviour
warnings.warn(
Downloading: "https://github.com/NVIDIA/DeepLearningExamples/zipball/torchhub" to /root/.cache/torch/hub/torchhub.zip
/root/.cache/torch/hub/NVIDIA_DeepLearningExamples_torchhub/PyTorch/Classification/ConvNets/image_classification/models/common.py:13: UserWarning: pytorch_quantization module not found, quantization will not be available
warnings.warn(
/root/.cache/torch/hub/NVIDIA_DeepLearningExamples_torchhub/PyTorch/Classification/ConvNets/image_classification/models/efficientnet.py:17: UserWarning: pytorch_quantization module not found, quantization will not be available
warnings.warn(
Downloading: "https://api.ngc.nvidia.com/v2/models/nvidia/waveglowpyt_fp32/versions/1/files/nvidia_waveglowpyt_fp32_20190306.pth" to /root/.cache/torch/hub/checkpoints/nvidia_waveglowpyt_fp32_20190306.pth
脚本总运行时间:(2 分 18.429 秒)